9 1 2 3 6
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 2.6 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.9 Clin Epidemiol
- 3.3 Cancer Manag Res
- 3.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.6 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.8 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.8 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 8.0 Int J Nanomed
- 2.3 Int J Women's Health
- 3.2 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 4.0 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.2 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.8 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.7 J Pain Res
- 3.3 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 4.3 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.9 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 3.5 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.5 J Inflamm Res
- 2.3 Int J Gen Med
- 4.1 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.2 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.3 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 3.3 J Multidiscip Healthc

白藜芦醇通过抑制 STAT3/HIF-1α/VEGF 信号通路遏制非小细胞肺癌(NSCLC)大鼠原位模型的肿瘤进展
Authors Wang H, Jia R, Lv T, Wang M, He S, Zhang X
Received 20 April 2020
Accepted for publication 5 June 2020
Published 21 July 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 7057—7063
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S259016
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Prof. Dr. Nicola Silvestris
Background: The STAT3/HIF-1α/VEGF pathway is associated with the development and progress of various tumors including NSCLC. The aim of the present study was to investigate whether resveratrol (RES) could suppress NSCLC progression via inhibiting the expressions of STAT3, HIF-1α, and VEGF in a nude rat model.
Methods: Twenty-four nude rats were randomly divided into control, NSCLC, and NSCLC+RES groups. An orthotopic rat model of NSCLC was established. The animals in the NSCLC+RES group received the same operation as the NSCLC group and were intragastrically administered RES at 250 mg/kg/day for 12 weeks. Lung tissue samples were harvested for gross tumor burden measurement, histological examinations, RT-PCR, and Western blot assays.
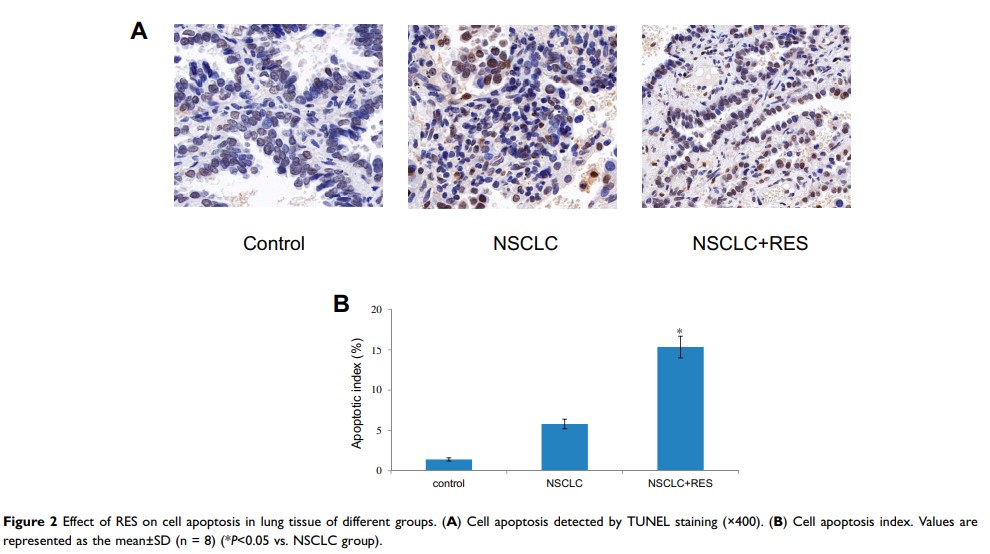
Results: In the NSCLC+RES group, significant decreases in lung weight index, lung tumor burden, STAT3/HIF-1α/VEGF mRNA, and protein levels were observed when compared with the NSCLC group (all P < 0.05). The structural integrity of the lung was less affected and the apoptotic index was significantly higher in the NSCLC+RES group, when compared to the NSCLC group (P < 0.05).
Conclusion: RES suppresses NSCLC partly through inhibiting the expressions of STAT3, HIF-1α, and VEGF. The STAT3/HIF-1α/VEGF pathway might be a candidate drug target for developing new chemotherapy agents derived from RES for the treatment of NSCLC.
Keywords: resveratrol, non-small-cell lung cancer, STAT3, HIF-1α, VEGF, rat