9 1 2 3 6
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 2.6 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.9 Clin Epidemiol
- 3.3 Cancer Manag Res
- 3.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.6 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.8 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.8 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 8.0 Int J Nanomed
- 2.3 Int J Women's Health
- 3.2 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 4.0 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.2 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.8 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.7 J Pain Res
- 3.3 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 4.3 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.9 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 3.5 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.5 J Inflamm Res
- 2.3 Int J Gen Med
- 4.1 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.2 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.3 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 3.3 J Multidiscip Healthc

长非编码 RNAADAMTS9-AS2 抑制膀胱肿瘤细胞的增殖、迁移和侵袭
Authors Zhang Z, Jia JP, Zhang YJ, Liu G, Zhou F, Zhang BC
Received 13 January 2020
Accepted for publication 29 May 2020
Published 21 July 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 7089—7100
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S245826
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Sanjay Singh
Background: Bladder tumor is the fifth most prevalent tumor in men, yet its pathogenesis remains to be fully identified. Albeit a host of long noncoding RNAs (lncRNA) are emerging as new players involved in bladder tumor, the functions of many lncRNAs are still enigmatic. Reports on the deluge of studies on lncRNA ADAMTS9-AS2 have been convincingly associated with various tumors, but without mention of its roles in bladder tumor. Therefore, the roles of ADAMTS9-AS2 in bladder tumor cells were explored in our study.
Materials and Methods: Quantitative real-time PCR assays and bioinformatic tools were applied in bladder tumor cells to identify the ADAMTS9-AS2 and ADAMTS9 expression. Western blot assays were performed to obtain the protein levels of bladder tumor related key molecules. CCK8, clonogenic assay, scratch wound healing, and transwell assays were separately applied to identify the functional roles of ADAMTS9-AS2 on proliferation, migration, and invasion in bladder tumor cells.
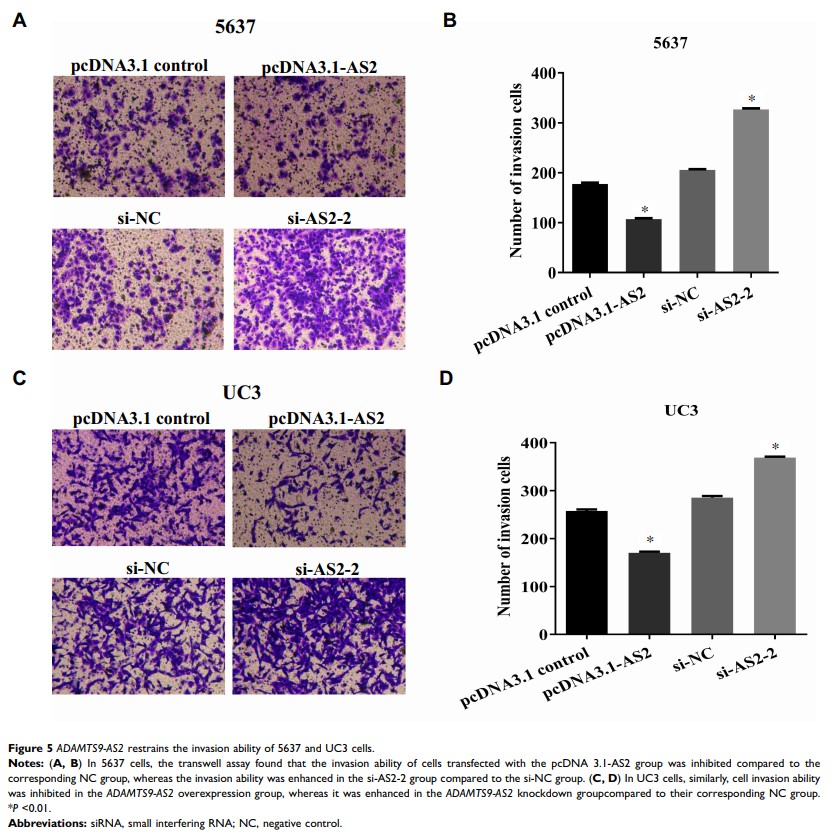
Results: First, ADAMTS9-AS2 downregulation in bladder tumor cells was identified. Overexpression and knockdown experiments showed that ADAMTS9-AS2 expression was positively related to ADAMTS9 , which is in accordance with the results from GEO database. Second, ADAMTS9-AS2 contributed to the inhibition of proliferation, migration, and invasion in bladder tumor cells. Third, ADAMTS9-AS2 was linked with PI3K /AKT /mTOR pathway related-molecules, several key autophagy, and apoptotic proteins.
Conclusion: Conjointly, our findings suggested that ADAMTS9-AS2 might function as a tumor suppressor to restrain the proliferation, migration, and invasion in bladder tumor cells. The potential mechanism of ADAMTS9-AS2 related to PI3K /AKT /mTOR signal pathway was further identified. Of note, we found that ADAMTS9-AS2 has a significant effect on several key autophagy and apoptotic proteins. Therefore, these observations will provide supportive evidence to ADAMTS9-AS2 as a potential biomarker in patients with bladder tumor.
Keywords: lncRNA ADAMTS9-AS2, proliferation, PI3K/AKT/mTOR, bladder tumor