9 1 2 3 6
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 2.6 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.9 Clin Epidemiol
- 3.3 Cancer Manag Res
- 3.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.6 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.8 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.8 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 8.0 Int J Nanomed
- 2.3 Int J Women's Health
- 3.2 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 4.0 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.2 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.8 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.7 J Pain Res
- 3.3 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 4.3 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.9 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 3.5 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.5 J Inflamm Res
- 2.3 Int J Gen Med
- 4.1 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.2 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.3 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 3.3 J Multidiscip Healthc

NLRP3 调节急性中性粒细胞肺损伤中 CXCL12 的表达
Authors Peng Y, Wu Q, Tang H, Chen J, Wu Q, Yuan X, Xiong S, Ye Y, Lv H
Received 30 April 2020
Accepted for publication 2 July 2020
Published 23 July 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 377—386
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/JIR.S259633
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Ning Quan
Background and Purpose: Both NLRP3 inflammasome and chemokines are involved in the initiation and development of acute lung inflammation, but the underlying mechanism is still elusive. The present study investigated the role of chemokines and NLRP3 in recruiting neutrophils in the early phase of acute lung injury.
Methods: In an endotoxin (lipopolysaccharide [LPS])-induced acute lung injury model, we measured the lung injury severity, myeloperoxidase (MPO) activity and chemokine profiles in wild-type (WT) and NLRP3 knockout (NLRP3–/–) mice, and then identified the key chemokines by specific antibody blockage.
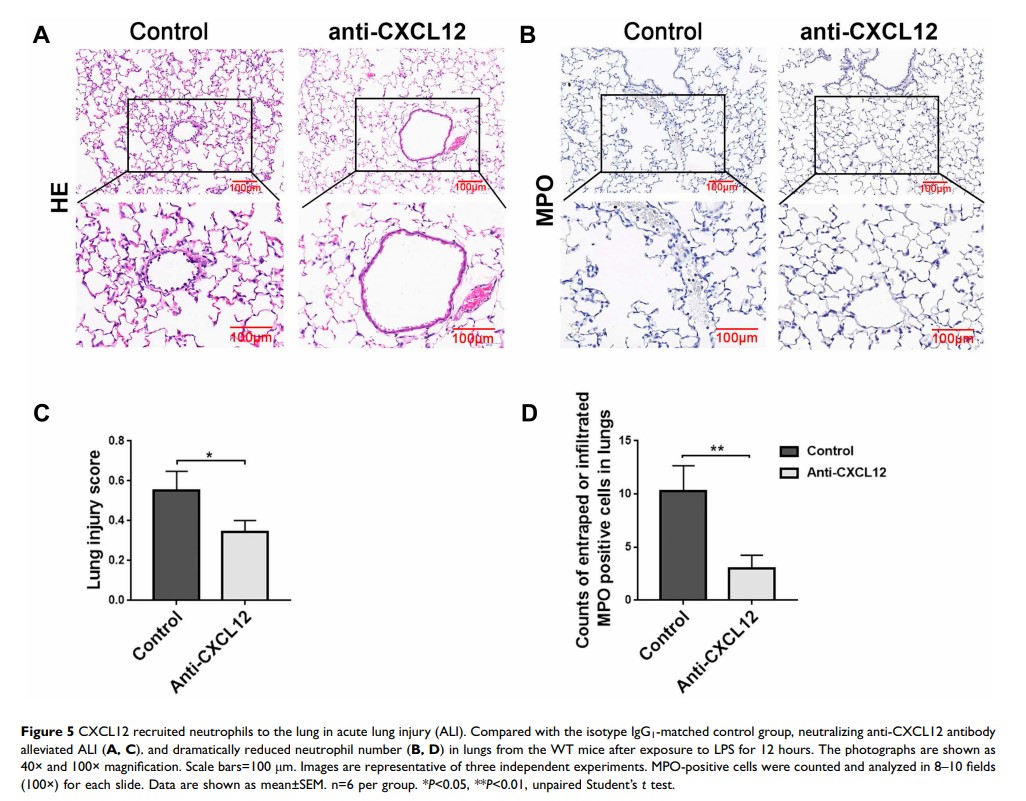
Results: The results showed that NLRP3 deficiency was associated with alleviating lung damage, by reducing alveolar epithelial cell apoptosis and decreasing neutrophil accumulation. Furthermore, compared with WT mice, IL-1β, CCL2, CXCL1, CXCL5 and CXCL12 levels from the serum of NLRP3–/– mice were much lower after exposure to LPS. However, in lung tissue, only lower CXCL12 levels were observed from the NLRP3–/– ALI mice, and higher levels of CXCR4 were expressed in NLRP3–/– neutrophils. Blockage of CXCL12 dramatically relieved the severity of ALI and reduced neutrophil accumulation in the lung.
Conclusion: NLRP3 alters CXCL12 expression in acute lung injury. CXCL12 is crucial for neutrophil recruitment in NLRP3-mediated neutrophilic lung injury.
Keywords: NLRP3, acute lung injury, ALI, neutrophils, chemokines, CXCL12