9 0 6 7 6
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 2.6 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.9 Clin Epidemiol
- 3.3 Cancer Manag Res
- 3.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.6 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.8 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.8 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 8.0 Int J Nanomed
- 2.3 Int J Women's Health
- 3.2 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 4.0 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.2 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.8 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.7 J Pain Res
- 3.3 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 4.3 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.9 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 3.5 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.5 J Inflamm Res
- 2.3 Int J Gen Med
- 4.1 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.2 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.3 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 3.3 J Multidiscip Healthc

新型咪唑并吡啶衍生物通过抑制 Wnt/βcatenin 信号传导发挥乳腺癌抗癌活性
Authors He LJ, Yang DL, Chen HY, Huang JH, Zhang YJ, Qin HX, Wang JL, Tang DY, Chen ZZ
Received 26 June 2020
Accepted for publication 1 September 2020
Published 9 October 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 10111—10121
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S266752
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Leo Jen-Liang Su
Background: Breast cancer exhibits poor prognosis and high relapse rates following chemotherapy therapeutics. Thus, this study aims to develop effective novel agents regulating the core molecular pathway of breast cancer such as Wnt/β-catenin signaling.
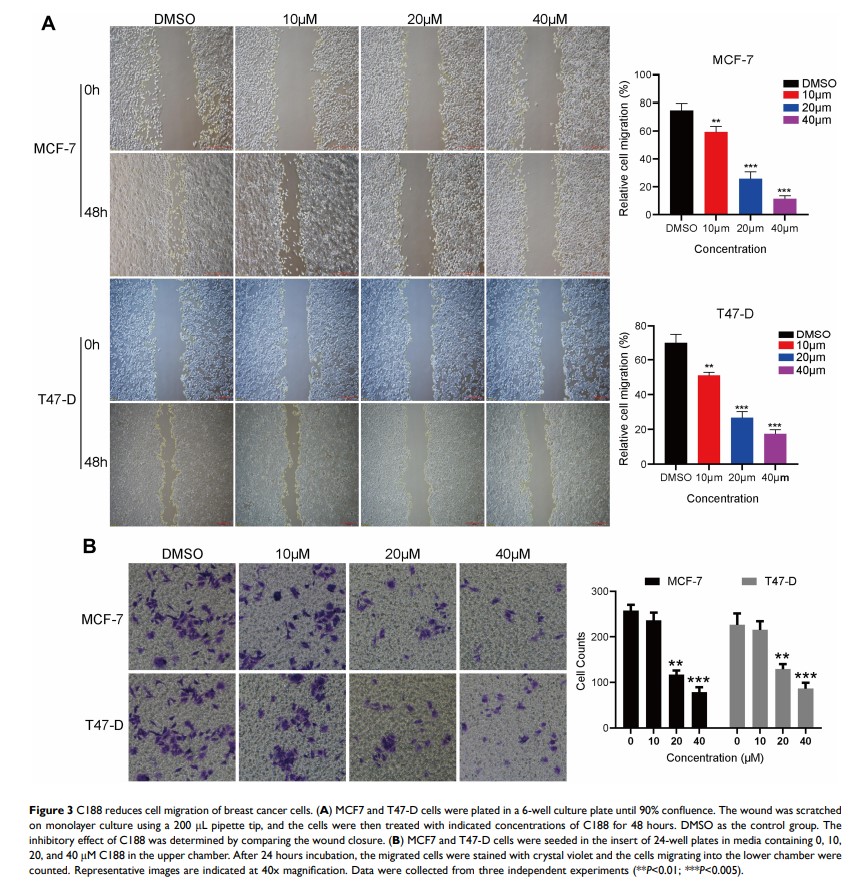
Methods: The present study screened a novel inhibitor, called “C188”, using MTT assay. The molecular formula of C188 is C21H15FN4O3 and the molecular weight is 390. Flow cytometry and Western blotting were employed to assess cell cycle arrest after treatment with C188. Wound-healing and transwell assays were applied to measure the cell migration and invasion viability. The regulatory effects of C188 on Wnt/β-catenin signaling and localization of β-catenin in the nucleus were investigated by Western blotting and immunofluorescence.
Results: We found that C188 significantly suppressed proliferation and growth in a dose- and time-dependent manner in breast cancer cells, but not in normal breast cells. The inhibitory effect was caused by cell cycle arrest at the G1-phase which is induced by C188 treatment. Additionally, C188 dramatically inhibited cell migration of breast cancer cells in a dose-dependent manner. The migration inhibition was attributed to the suppression of Wnt/β-catenin signaling and localization of β-catenin in the nucleus mediated by regulating phosphorylation of β-catenin and its subsequent stability. Furthermore, the target genes, including Axin 2 , c-JUN , and c-Myc , were downregulated due to the decrease of β-catenin in the nucleus after exposure to C188.
Conclusion: C188 treatment resulted in the downregulation of cyclin D which led to cell cycle arrest at the G1 phase, and the inhibition of cell migration, indicating that C188 may be an effective novel therapeutic candidate as a potential treatment for human breast cancer.
Keywords: C188, breast cancer, proliferation, cell cycle, cell migration, Wnt/β-catenin