9 0 7 9 9
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 2.6 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.9 Clin Epidemiol
- 3.3 Cancer Manag Res
- 3.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.6 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.8 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.8 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 8.0 Int J Nanomed
- 2.3 Int J Women's Health
- 3.2 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 4.0 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.2 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.8 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.7 J Pain Res
- 3.3 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 4.3 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.9 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 3.5 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.5 J Inflamm Res
- 2.3 Int J Gen Med
- 4.1 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.2 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.3 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 3.3 J Multidiscip Healthc

小白菊内酯 (Parthenolide) 通过自噬介导的凋亡抑制胰腺细胞生长
Authors Liu W, Wang X, Sun J, Yang Y, Li W, Song J
Received 14 July 2016
Accepted for publication 17 September 2016
Published 23 January 2017 Volume 2017:10 Pages 453—461
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S117250
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Akshita Wason
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Samir Farghaly
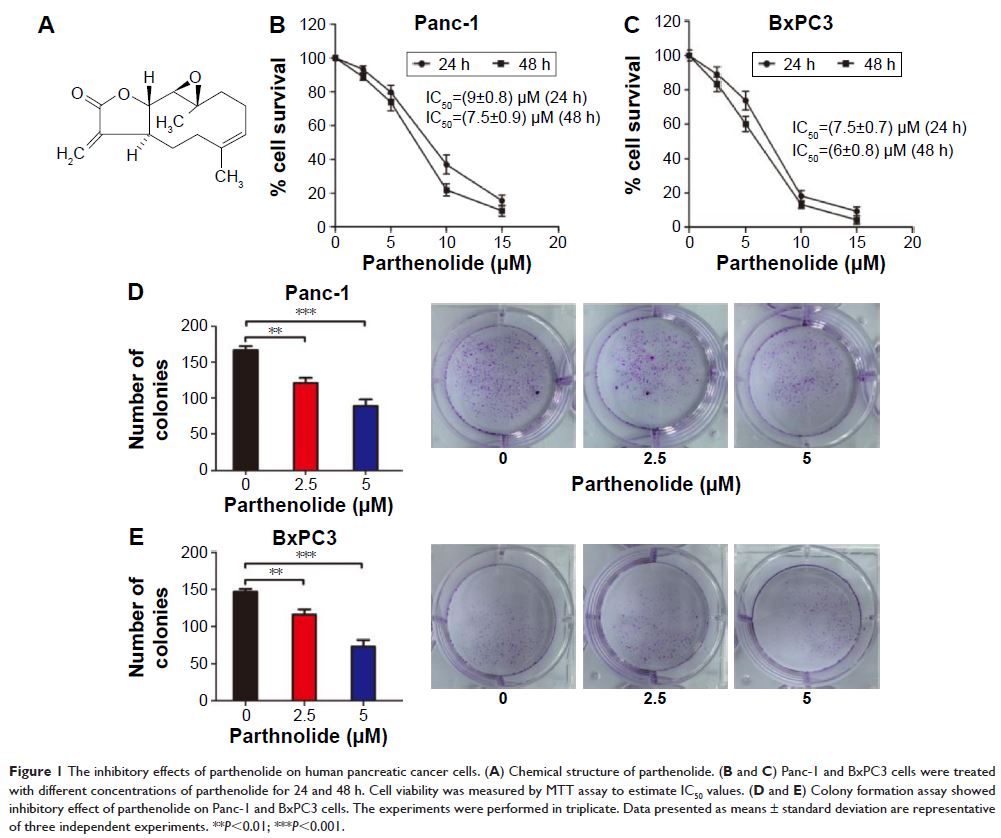
Abstract: Pancreatic cancer is an aggressive malignancy and is unresponsive to
conventional chemotherapies. Parthenolide, a sesquiterpene lactone isolated
from feverfew, has exhibited potent anticancer effects against various cancers.
The purpose of this report was to investigate the effect and underlying
mechanism of parthenolide in human pancreatic cancer Panc-1 and BxPC3 cells.
The results demonstrated that parthenolide suppressed the growth and induced
apoptosis of Panc-1 and BxPC3 pancreatic cancer cells with the half maximal
inhibitory concentration (IC50) ranging
between 7 and 9 µM after 24 h of treatment. Significant autophagy was induced
by parthenolide treatment in pancreatic cancer cells. Parthenolide treatment
concentration-dependently increased the percentage of autophagic cells and
significantly increased the expression levels of p62/SQSTM1, Beclin 1, and
LC3II in Panc-1 cells. Punctate LC3II staining confirmed autophagy.
Furthermore, inhibiting autophagy by chloroquine, 3-methyladenine, or LC3II
siRNA significantly blocked parthenolide-induced apoptosis, suggesting that
parthenolide induced apoptosis through autophagy in this study. In conclusion,
these studies established that parthenolide inhibits pancreatic cell growth by
autophagy-mediated apoptosis. Data of the present study suggest that
parthenolide can serve as a potential chemotherapeutic agent for pancreatic
cancer.
Keywords: parthenolide, pancreatic cancer,
autophagy, apoptosis, P62, cleaved PAPRP