9 0 8 0 2
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 2.6 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.9 Clin Epidemiol
- 3.3 Cancer Manag Res
- 3.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.6 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.8 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.8 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 8.0 Int J Nanomed
- 2.3 Int J Women's Health
- 3.2 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 4.0 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.2 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.8 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.7 J Pain Res
- 3.3 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 4.3 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.9 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 3.5 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.5 J Inflamm Res
- 2.3 Int J Gen Med
- 4.1 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.2 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.3 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 3.3 J Multidiscip Healthc

人源化 CD7 纳米体系免疫毒素表现出攻克 T 细胞型急性淋巴细胞白血病的潜力
Authors Yu Y, Li J, Zhu X, Tang X, Bao Y, Sun X, Huang Y, Tian F, Liu X, Yang L
Received 13 November 2016
Accepted for publication 13 February 2017
Published 13 March 2017 Volume 2017:12 Pages 1969—1983
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S127575
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Lakshmi Kiran Chelluri
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
Background: Nanobodies,
named as VHHs (variable domain of heavy chain of HCAb [heavy-chain
antibodies]), are derived from heavy-chain-only antibodies that circulate in
sera of camelids. Their exceptional physicochemical properties, possibility of
humanization, and unique antigen recognition properties make them excellent
candidates for targeted delivery of biologically active components, including
immunotoxins. In our previous efforts, we have successfully generated the
monovalent and bivalent CD7 nanobody-based immunotoxins, which can effectively
trigger the apoptosis of CD7-positive malignant cells. To pursue the
possibility of translating those immunotoxins into clinics, we humanized the
nanobody sequences (designated as dhuVHH6) as well as further truncated the Pseudomonas exotoxin A (PE)-derived PE38 toxin to
produce a more protease-resistant form, which is named as PE-LR, by deleting
majority of PE domain II.
Methods and results: Three new types of immunotoxins, dhuVHH6-PE38,
dVHH6-PE-LR, and dhuVHH6-PE-LR, were successfully constructed. These
recombinant immunotoxins were expressed in Escherichia coli and showed that nanobody immunotoxins
have the benefits of easy soluble expression in a prokaryotic expression
system. Flow cytometry results revealed that all immunotoxins still maintained the
ability to bind specifically to CD7-positive T lymphocyte strains without
binding to CD7-negative control cells. Laser scanning confocal microscopy
revealed that these proteins can be endocytosed into the cytoplasm after
binding with CD7-positive cells and that this phenomenon was not observed in
CD7-negative cells. WST-8 experiments showed that all immunotoxins retained the
highly effective and specific growth inhibition activity in CD7-positive cell
lines and primary T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (T-ALL) cells. Further in
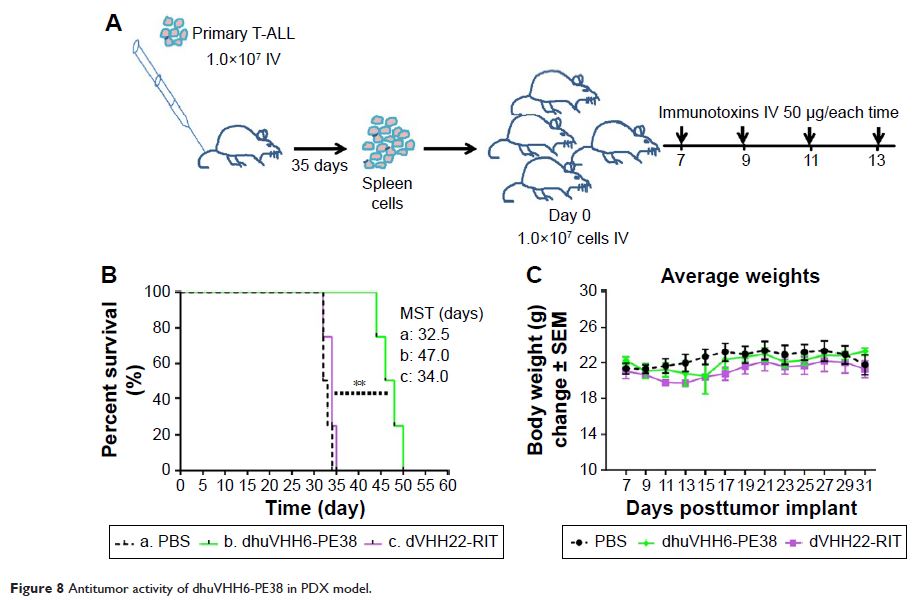
vivo animal model experiments showed that humanized dhuVHH6-PE38 immunotoxin
can tolerate higher doses and extend the survival of NOD-Prkdcem26Il2rgem26Nju (NCG) mice
transplanted with CEM cells without any obvious decrease in body weight.
Further studies on NCG mice model with patient-derived T-ALL cells,
dhuVHH6-PE38 treatment, significantly prolonged mice survival with ~40%
survival improvement. However, it was also noticed that although dhuVHH6-PE-LR
showed strong antitumor effect in vitro, its in vivo antitumor efficacy was
disappointing.
Conclusion: We have successfully constructed a targeted CD7
molecule-modified nanobody (CD7 molecule-improved nanobody) immunotoxin
dhuVHH6-PE38 and demonstrated its potential for treating CD7-positive malignant
tumors, especially T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia.
Keywords: CD7, humanized nanobody, T-cell acute
lymphoblastic leukemia, patient-derived xenograft model, recombinant
immunotoxins, Pseudomonas exotoxin A