9 0 8 0 2
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 2.6 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.9 Clin Epidemiol
- 3.3 Cancer Manag Res
- 3.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.6 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.8 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.8 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 8.0 Int J Nanomed
- 2.3 Int J Women's Health
- 3.2 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 4.0 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.2 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.8 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.7 J Pain Res
- 3.3 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 4.3 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.9 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 3.5 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.5 J Inflamm Res
- 2.3 Int J Gen Med
- 4.1 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.2 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.3 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 3.3 J Multidiscip Healthc

PI3K 和 mTOR 双重抑制剂 NVP-BEZ235 与甲磺酸伊马替尼 (imatinib) 联合用于慢性髓细胞白血病细胞系的疗效
Authors Xin P, Li C, Zheng Y, Peng Q, Xiao H, Huang Y, Zhu X
Received 10 January 2017
Accepted for publication 10 February 2017
Published 3 April 2017 Volume 2017:11 Pages 1115—1126
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S132092
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Junhua Mai
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Tuo Deng
Background: Phosphatidylinositol
3-kinase/Akt/mammalian target of rapamycin (PI3K/Akt/mTOR) pathway is a therapy
target of cancer. We aimed to confirm the effect of dual PI3K/mTOR inhibitor
NVP-BEZ235 on proliferation, apoptosis, and autophagy of chronic myelogenous
leukemia (CML) cells and sensitivity of tyrosine kinase inhibitor in vitro.
Methods: Two human CML cell lines, K562 and KBM7R (T315I mutant
strain), were used. The proliferation of CML cells was detected by MTS (Owen’s
reagent) assay. Cell cycle and apoptosis assay were examined by flow cytometric
analysis. The phosphorylation levels and the expression levels were both
evaluated by Western blot analysis. NVP-BEZ235 in combination with imatinib was
also used to reveal the effect on proliferation and apoptosis.
Results: NVP-BEZ235 significantly inhibited the proliferation
in a time- and dose-dependent manner, and the half-maximal inhibitory
concentration values of NVP-BEZ235 inhibiting the proliferation of K562 and
KBM7R were 0.37±0.21 and 0.43±0.27 µmol/L, respectively, after 48 h. Cell
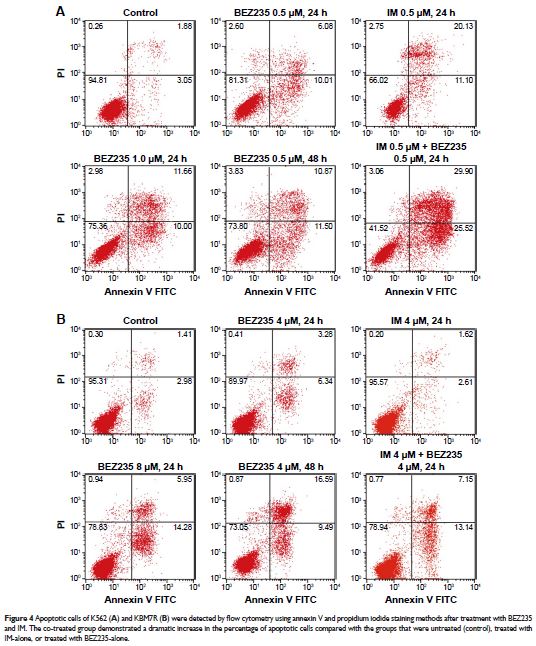
apoptosis assay showed that NVP-BEZ235 significantly increased the late
apoptotic cells. Cell cycle analysis indicated that the cells were mostly
arrested in G1/G0 phase after treatment by NVP-BEZ235. In addition, results
also found that, after treatment by NVP-BEZ235, phosphorylation levels of Akt
kinase and S6K kinase significantly reduced, and the expression levels of
cleaved caspase-3 significantly increased; meanwhile, the expression levels of
caspase-3, B-cell lymphoma-2, cyclin D1, and cyclin D2 significantly decreased,
and the ratio of LC3II/LC3I was significantly increased with increased LC3II
expression level. Moreover, imatinib in combination with NVP-BEZ235 induced a
more pronounced colony growth inhibition than imatinib alone.
Conclusion: NVP-BEZ235 effectively inhibited cell proliferation by
G0/G1 cell cycle arrest and induced apoptosis through deregulating
PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway in CML cells; in addition, NVP-BEZ235 can enhance cell
autophagy, and is conducive to raising CML cell sensitivity to imatinib to
inhibit the growth of imatinib-resistant cells.
Keywords: chronic myelogenous leukemia,
NVP-BEZ235, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt/mammalian pathway, imatinib,
apoptosis, autophagy