9 0 8 0 2
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 2.6 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.9 Clin Epidemiol
- 3.3 Cancer Manag Res
- 3.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.6 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.8 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.8 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 8.0 Int J Nanomed
- 2.3 Int J Women's Health
- 3.2 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 4.0 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.2 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.8 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.7 J Pain Res
- 3.3 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 4.3 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.9 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 3.5 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.5 J Inflamm Res
- 2.3 Int J Gen Med
- 4.1 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.2 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.3 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 3.3 J Multidiscip Healthc

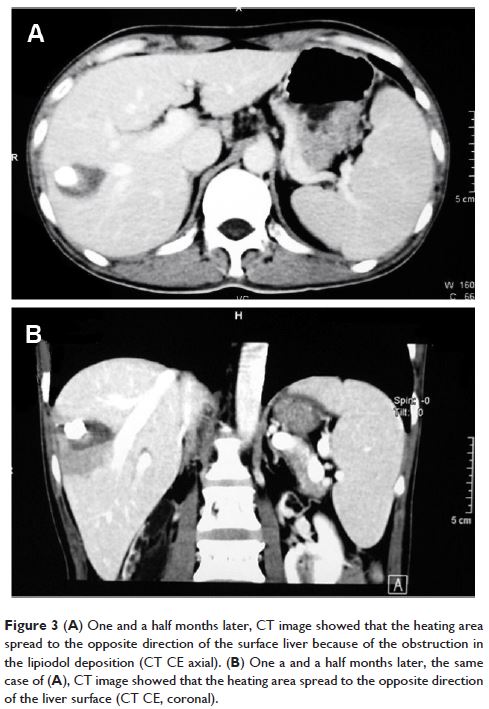
TACE 之后 HCC 中的脂质沉积对 PMCT 坏死范围的影响
Authors Sun HL, Ni JY, Jiang XY, Chen D, Chen YT, Xu LF
Received 17 March 2017
Accepted for publication 19 June 2017
Published 1 August 2017 Volume 2017:10 Pages 3835—3842
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S137312
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Yao Dai
Objective: To study the impact of lipiodol deposition in the lesion of
hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) after transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) on
the necrosis area of percutaneous microwave coagulation therapy (PMCT).
Materials and methods: A total of 44 patients with HCC with 56 nodules,
with a size ranging from 1.5 to 3.5 cm, was selected in our study. About 23
patients (26 nodules) underwent PMCT treatment only as Group A and 21 patients
(30 nodules) were treated by PMCT-combined TACE as Group B. All patients
underwent PMCT with single-electrode and one-point ablation. Paired t-test was used to analyze pre-
and postoperatively the volume of tumor and the necrosis volume after PMCT.
Independent t-test was used to compare the
difference in the necrosis area between two groups (α=0.05).
Results: All patients underwent PMCT or PMCT combined with TACE
successfully. The tumor and necrosis size of Group A was 16.29±19.23 cm3 and 17.98±18.49 cm3 (P =0.650), and 11.95±12.78 cm3 and 16.60±11.70 cm3 of
Group B (P =0.017). There was no significant
difference on necrosis volume between the two groups (P =0.581). The necrosis area of
Group B was larger than the size of the tumor (P =0.017),
but the ablation area of the two groups was smaller than the theoretic area (P =0.001). (The theoretic area
means that the necrosis area of ablation should be 1.0 cm larger than the tumor
in diameter.)
Conclusion: PMCT combined with TACE could enlarge the ablation
area, but will not lead to an ideal necrosis area than the PMCT alone. The
lipiodol deposition in the tumor lesion may hinder the expansion of the heating
field. Therefore, further research was needed.
Keywords: hepatocellular
carcinoma, transarterial chemoembolization, percutaneous microwave coagulation
therapy, lipiodol