9 0 8 0 2
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 2.6 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.9 Clin Epidemiol
- 3.3 Cancer Manag Res
- 3.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.6 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.8 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.8 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 8.0 Int J Nanomed
- 2.3 Int J Women's Health
- 3.2 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 4.0 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.2 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.8 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.7 J Pain Res
- 3.3 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 4.3 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.9 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 3.5 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.5 J Inflamm Res
- 2.3 Int J Gen Med
- 4.1 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.2 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.3 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 3.3 J Multidiscip Healthc

已发表论文
RACK1 通过上调 PI3K/AKT 通路和 Bcl-2 表达来诱导食管癌的化疗耐药
Authors Liu B, Wang C, Chen P, Cheng B, Cheng Y
Received 28 September 2017
Accepted for publication 28 November 2017
Published 4 January 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 211—220
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S152818
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Federico Perche
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Ingrid Espinoza
Introduction: Accumulating
evidence indicates that RACK1 is involved in the progression of tumors. We
aimed to evaluate the function of RACK1 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
(ESCC) and its role in the mechanism of chemotherapy resistance.
Materials and methods: Transfected ESCC cell lines with plasmids expressed shRACK1 or open reading frame (ORF) targeting RACK1 and established stable cell lines. We then examined the effects of RACK1 on cell proliferation and chemotherapy resistance in ESCC cell lines, and the expression of AKT, pAKT, ERK1/2, Bcl-2, and Bim was introduced to further detect the association between RACK1 and chemotherapy resistance.
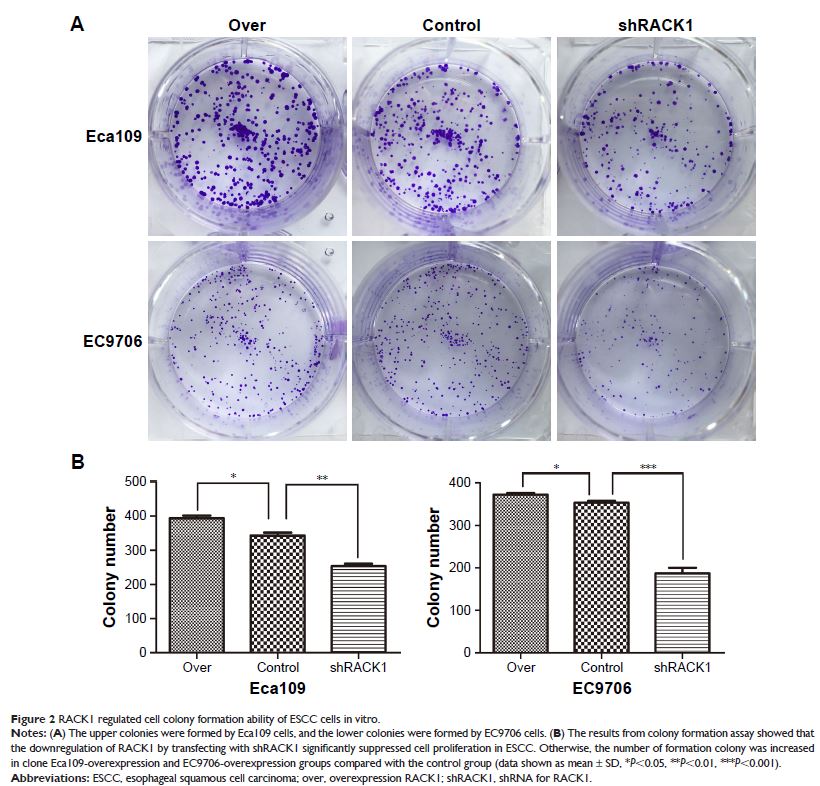
Results: The proliferation ability of ESCC cells was improved in the overexpression RACK1 groups (P <0.001) and decreased in the transfected shRACK1 groups (P <0.001) compared with the control ones. Meanwhile, upregulation of RACK1 significantly suppressed cisplatin-induced apoptosis in Eca109 and EC9706 cells, while downregulation of RACK1 promoted the sensitivity compared to the control group (Eca109: P <0.001 for shRACK1, P <0.01 for shNC, and P <0.001 for overexpression group; EC9706: P <0.001 for shRACK1, P <0.001 for shNC, and P <0.05 for overexpression group). Furthermore, we found that RACK1 could activate the PI3K/AKT pathway and increase the expression level of Bcl-2 in ESCC, which leads to the enhancement of chemoresistance in ESCC.
Conclusion: RACK1 promotes proliferation and chemotherapy resistance in ESCC by activating the PI3K/AKT pathway and upregulating the Bcl-2 expression.
Keywords: RACK1, ESCC, chemotherapy resistance, PI3K/AKT pathway, Bcl-2
Materials and methods: Transfected ESCC cell lines with plasmids expressed shRACK1 or open reading frame (ORF) targeting RACK1 and established stable cell lines. We then examined the effects of RACK1 on cell proliferation and chemotherapy resistance in ESCC cell lines, and the expression of AKT, pAKT, ERK1/2, Bcl-2, and Bim was introduced to further detect the association between RACK1 and chemotherapy resistance.
Results: The proliferation ability of ESCC cells was improved in the overexpression RACK1 groups (P <0.001) and decreased in the transfected shRACK1 groups (P <0.001) compared with the control ones. Meanwhile, upregulation of RACK1 significantly suppressed cisplatin-induced apoptosis in Eca109 and EC9706 cells, while downregulation of RACK1 promoted the sensitivity compared to the control group (Eca109: P <0.001 for shRACK1, P <0.01 for shNC, and P <0.001 for overexpression group; EC9706: P <0.001 for shRACK1, P <0.001 for shNC, and P <0.05 for overexpression group). Furthermore, we found that RACK1 could activate the PI3K/AKT pathway and increase the expression level of Bcl-2 in ESCC, which leads to the enhancement of chemoresistance in ESCC.
Conclusion: RACK1 promotes proliferation and chemotherapy resistance in ESCC by activating the PI3K/AKT pathway and upregulating the Bcl-2 expression.
Keywords: RACK1, ESCC, chemotherapy resistance, PI3K/AKT pathway, Bcl-2