9 0 8 0 2
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 2.6 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.9 Clin Epidemiol
- 3.3 Cancer Manag Res
- 3.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.6 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.8 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.8 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 8.0 Int J Nanomed
- 2.3 Int J Women's Health
- 3.2 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 4.0 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.2 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.8 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.7 J Pain Res
- 3.3 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 4.3 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.9 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 3.5 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.5 J Inflamm Res
- 2.3 Int J Gen Med
- 4.1 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.2 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.3 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 3.3 J Multidiscip Healthc

EZH2 的四种单核苷酸多态性对癌症风险的影响:系统评价和荟萃分析
Authors Ling Z, You Z, Hu L, Zhang L, Wang Y, Zhang M, Zhang G, Chen S, Xu B, Chen M
Received 27 November 2017
Accepted for publication 30 December 2017
Published 16 February 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 851—865
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S158173
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Carlos Vigil Gonzales
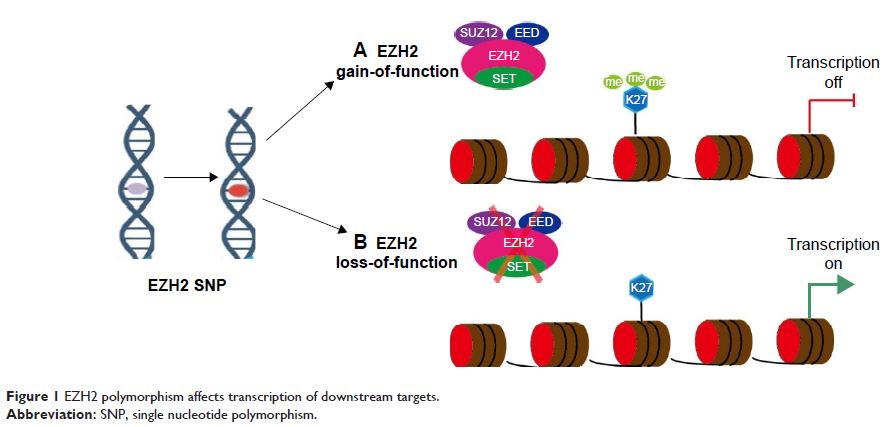
Background: Although the relationship between several single nucleotide
polymorphisms (SNPs) of the oncogene EZH2 and
cancer risk has been assessed by some case–control studies, results of
subsequent studies are controversial. Sample sizes from single-center studies
are also limited, thereby providing unreliable findings. Hence, we conducted a
comprehensive search and meta-analysis to evaluate the associations
between EZH2 SNPs and cancer risk.
Materials and
methods: A comprehensive literature search
for studies focusing on EZH2 SNPs and
cancer risk was conducted on PubMed, Web of Science, Embase, and China National
Knowledge Infrastructure online databases. Genotype data were extracted and
examined through a meta-analysis, and pooled odds ratios (ORs) with 95% CIs
were used to assess the corresponding associations. Sensitivity analysis,
publication bias assessment, and heterogeneity test were performed using STATA
12.0.
Results: Twelve eligible studies were included in this meta-analysis. The
association of 4 SNPs, namely, rs887569, rs2302427, rs3757441, and rs41277434,
in the EZH2 locus with cancer risk
was evaluated. Five studies (1,794 cases and 1,878 controls) indicated that
rs887569 was related to a decreased cancer risk (CTTT/CC: OR =0.849, 95% CI:
[0.740 to 0.973], P =0.019; TT/CCCT:
OR =0.793, 95% CI: [0.654 to 0.962], P =0.019). Seven
studies (2,408 cases and 2,910 controls) showed that rs2302427 was linked to a
decreased cancer risk (GG/CC: OR =0.562, 95% CI: [0.400 to 0.792], P =0.001; CGGG/CC: OR =0.856, 95%
CI: [0.748 to 0.980], P =0.024; GG/CCCG:
OR =0.733, 95% CI: [0.571 to 0.940], P =0.015). No
relationships were observed between rs3757441 or rs41277434 and cancer risk.
Conclusion: rs887569 and rs2302427 in EZH2 may be
correlated with a decreased cancer risk. Although rs3757441 and rs41277434 are
independent risk factors of cancer, further large-scale and functional studies
are warranted to validate our findings.
Keywords: EZH2, single nucleotide polymorphism, cancer risk, meta-analysis