9 0 8 0 2
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 2.6 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.9 Clin Epidemiol
- 3.3 Cancer Manag Res
- 3.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.6 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.8 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.8 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 8.0 Int J Nanomed
- 2.3 Int J Women's Health
- 3.2 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 4.0 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.2 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.8 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.7 J Pain Res
- 3.3 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 4.3 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.9 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 3.5 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.5 J Inflamm Res
- 2.3 Int J Gen Med
- 4.1 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.2 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.3 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 3.3 J Multidiscip Healthc

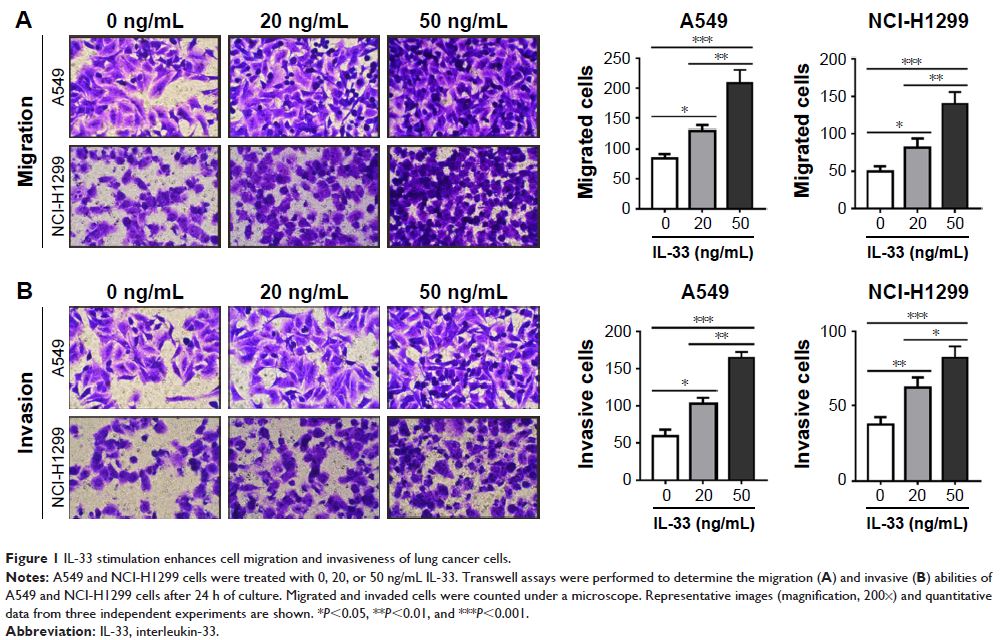
白细胞介素-33 可增强人肺癌细胞的迁移和侵袭力
Authors Yang Z, Gao X, Wang J, Xu L, Zheng Y, Xu Y
Received 2 November 2017
Accepted for publication 15 December 2017
Published 16 February 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 843—849
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S155905
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Justinn Cochran
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Yao Dai
Aim: Interleukin-33 (IL-33),
belonging to IL-1 family cytokines, has been reported to participate in cancer
growth and metastasis. The clinical values of IL-33 in lung cancer have been
previously investigated. We aimed to elucidate the probable role of IL-33 in
the migration and invasion of lung cancer cells.
Methods: Cell migration and invasiveness were tested by
Transwell assay. Western blotting analysis was performed to detect protein
expression.
Results: We found that IL-33 treatment in human lung A549 cells
dose-dependently enhanced their migratory and invasive ability, accompanied by
elevated expression of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) 2 and MMP9. Meanwhile,
IL-33-induced cell migration and invasion were significantly abolished by small
interfering RNA-targeting ST2, the specific receptor of IL-33. Furthermore,
IL-33 exposure induced the phosphorylation of AKT. Pretreatment with an AKT
inhibitor LY294002 markedly attenuated IL-33-induced cell migration and
invasion.
Conclusion: IL-33/ST2 promoted the migration and invasiveness of
lung cancer cells through AKT pathway. Our findings strongly suggest that IL-33
may serve as a promising therapeutic strategy for lung cancer.
Keywords: ST2, AKT,
migration, invasion