9 0 8 0 2
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 2.6 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.9 Clin Epidemiol
- 3.3 Cancer Manag Res
- 3.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.6 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.8 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.8 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 8.0 Int J Nanomed
- 2.3 Int J Women's Health
- 3.2 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 4.0 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.2 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.8 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.7 J Pain Res
- 3.3 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 4.3 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.9 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 3.5 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.5 J Inflamm Res
- 2.3 Int J Gen Med
- 4.1 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.2 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.3 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 3.3 J Multidiscip Healthc

2-亚苄基-1-茚酮衍生物作为治疗急性肺损伤抗炎剂的设计、合成和构效关系
Authors Xiao S, Zhang W, Chen H, Fang B, Qiu Y, Chen X, Chen L, Shu S, Zhang Y, Zhao Y, Liu Z, Liang G
Received 19 December 2017
Accepted for publication 16 February 2018
Published 19 April 2018 Volume 2018:12 Pages 887—899
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S160314
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Palas Chanda
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Qiongyu Guo
Purpose: The
purpose of this study was to design and synthesize novel
2-benzylidene-1-indanone derivatives for treatment of acute lung injury.
Methods: A series of 39 novel 2-benzylidene-indanone structural derivatives
were synthesized and evaluated for anti-inflammatory activity in
lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated murine primary macrophages.
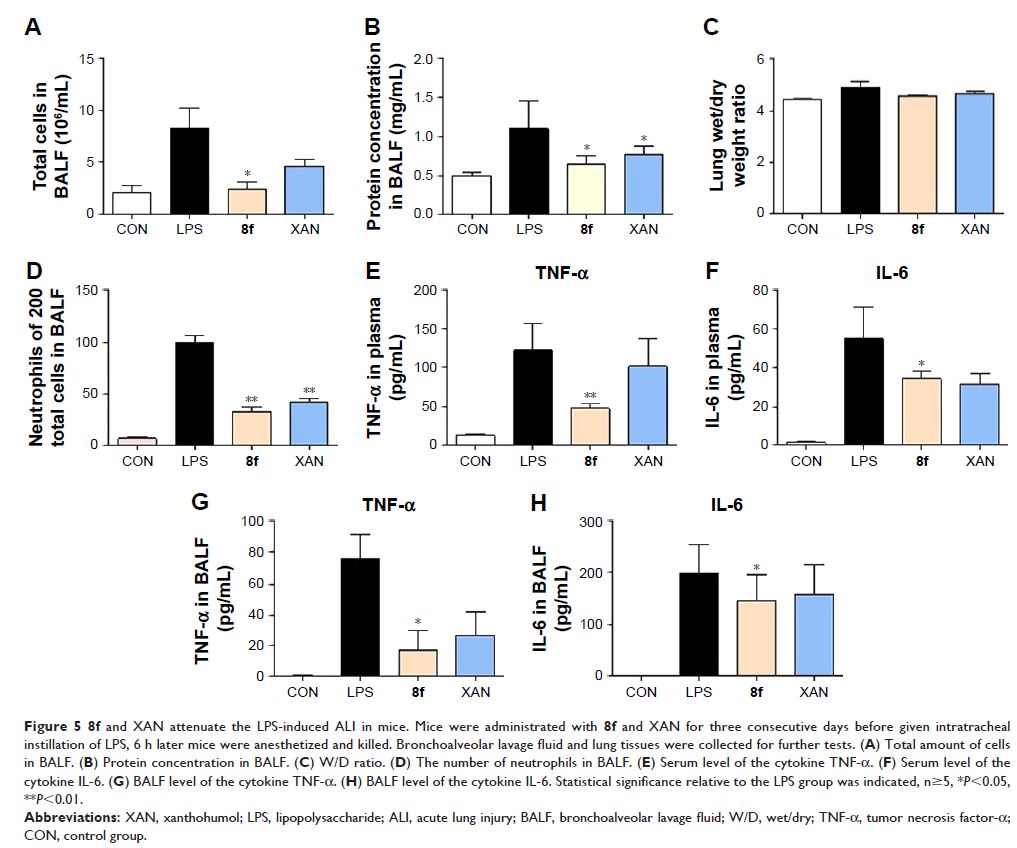
Results: Most of the obtained compounds effectively inhibited the
LPS-induced expression of IL-6 and TNF-α. The most active compound, 8f, was
found to significantly reduce LPS-induced pulmonary inflammation, as reflected
by reductions in the concentration of total protein, inflammatory cell count,
as well as the lung wet/dry ratio in bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) fluid.
Furthermore, 8f effectively inhibited mRNA expression of several inflammatory
cytokines after LPS challenge in vitro and in vivo. Administration of 8f also
blocked LPS-induced activation of the proinflammatory NF-κB/MAPK signaling
pathway.
Conclusion: The simple synthetic preparation and biological properties of
these derivatives make these 2-benzylidene-indanone scaffolds promising new
entities for the development of anti-inflammatory therapeutics for the
treatment of acute lung injury.
Keywords: indanone, acute lung injury, drug design, anti-inflammation,
synthesis