9 0 8 0 2
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 2.6 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.9 Clin Epidemiol
- 3.3 Cancer Manag Res
- 3.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.6 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.8 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.8 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 8.0 Int J Nanomed
- 2.3 Int J Women's Health
- 3.2 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 4.0 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.2 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.8 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.7 J Pain Res
- 3.3 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 4.3 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.9 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 3.5 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.5 J Inflamm Res
- 2.3 Int J Gen Med
- 4.1 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.2 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.3 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 3.3 J Multidiscip Healthc

富亮氨酸 α2 糖蛋白 1 可在结肠直肠癌中上调并且是肿瘤启动子
Authors Zhang Q, Huang R, Tang Q, Yu Y, Huang Q, Chen Y, Wang G, Wang X
Received 6 October 2017
Accepted for publication 13 December 2017
Published 11 May 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 2745—2752
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S153375
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Ru Chen
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Carlos Vigil Gonzales
Background: Leucine-rich α-2-glycoprotein-1 (LRG1) is differentially expressed
in many kinds of diseases including cancer, however, it has not been thoroughly
studied yet.
Purpose: The objective of this study was to detect the expression and
potential mechanism of LRG1 in colorectal cancer (CRC). In our study, we
examined LRG1 levels in CRC tissue and plasma with quantitative real-time
polymerase chain reaction and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, respectively.
The effect of LRG1 on cancer cells was detected with transwell and MTT assays.
Results: The average plasma LRG1 level in CRC was significantly higher than
in polyp group (P =0.002) and healthy controls (P <0.001). Second, plasma LRG1
was positively associated with CA19-9 (r =0.133, P =0.039) and neutrophil ratio (r =0.403, P <0.001). Third, plasma LRG1 of
stage IV patients was dramatically different from that of stage I, stage II or
stage III patients (P <0.001). LRG1
mRNA expression levels were about 2-fold higher in CRCs compared to normal
tissues (P <0.001). And levels of plasma
LRG1 were found to be a risk factor in CRC in univariate survival analysis of
colorectal prognosis (P =0.013, hazard
ratio [HR]=1.803, 95% CI: 1.521–2.137), and multivariate analysis showed that
LRG1 was an independent risk factor (P <0.001,
HR=1.492, 95% CI: 1.223–1.820). The patients with higher plasma LRG1 value
presented with poorer outcome (P =0.013).
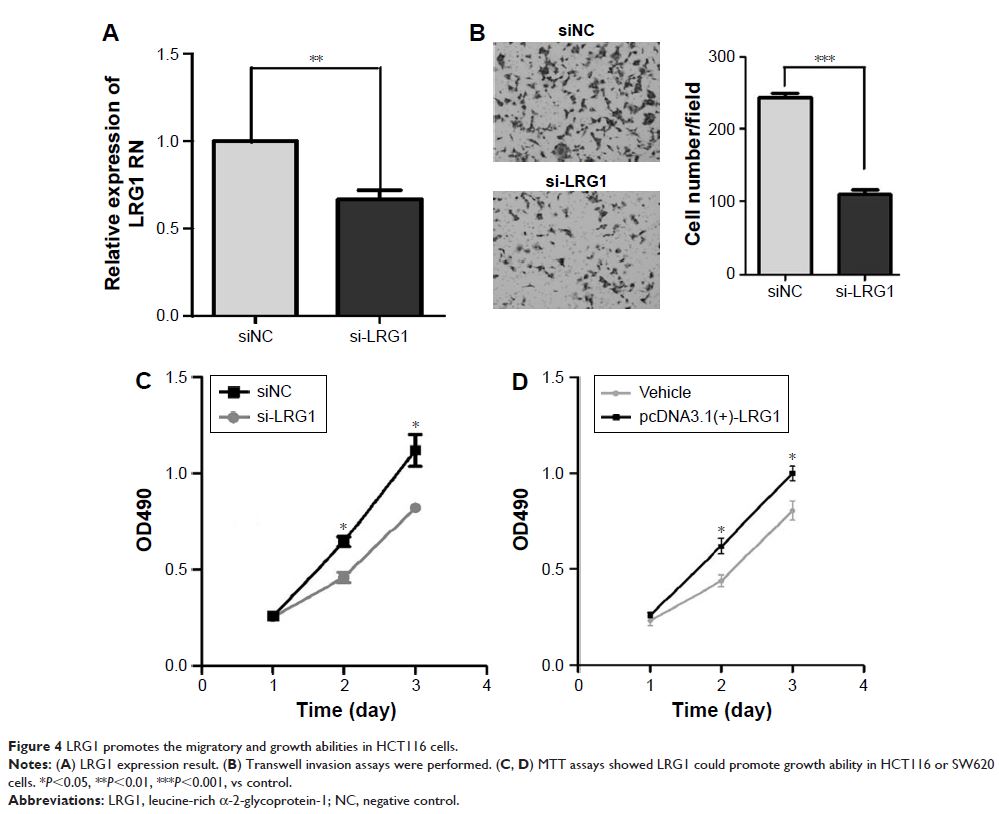
Functional experiments showed that LRG1 could promote the invasion and growth ability
of cells. LRG1 was increased in plasma and tissue compared with that of
controls and LRG1 may predict prognosis of CRC patients and LRG1 maybe a tumor
promoter.
Conclusion: LRG1 is increased in CRC patients and might serve as a tumor
promoter.
Keywords: adenomatous polyps, CA19-9 antigen, colorectal neoplasms,
leucine-rich alpha-2-glycoprotein, prognosis, tumor promoter