9 0 9 6 8
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 2.6 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.9 Clin Epidemiol
- 3.3 Cancer Manag Res
- 3.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.6 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.8 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.8 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 8.0 Int J Nanomed
- 2.3 Int J Women's Health
- 3.2 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 4.0 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.2 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.8 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.7 J Pain Res
- 3.3 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 4.3 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.9 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 3.5 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.5 J Inflamm Res
- 2.3 Int J Gen Med
- 4.1 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.2 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.3 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 3.3 J Multidiscip Healthc

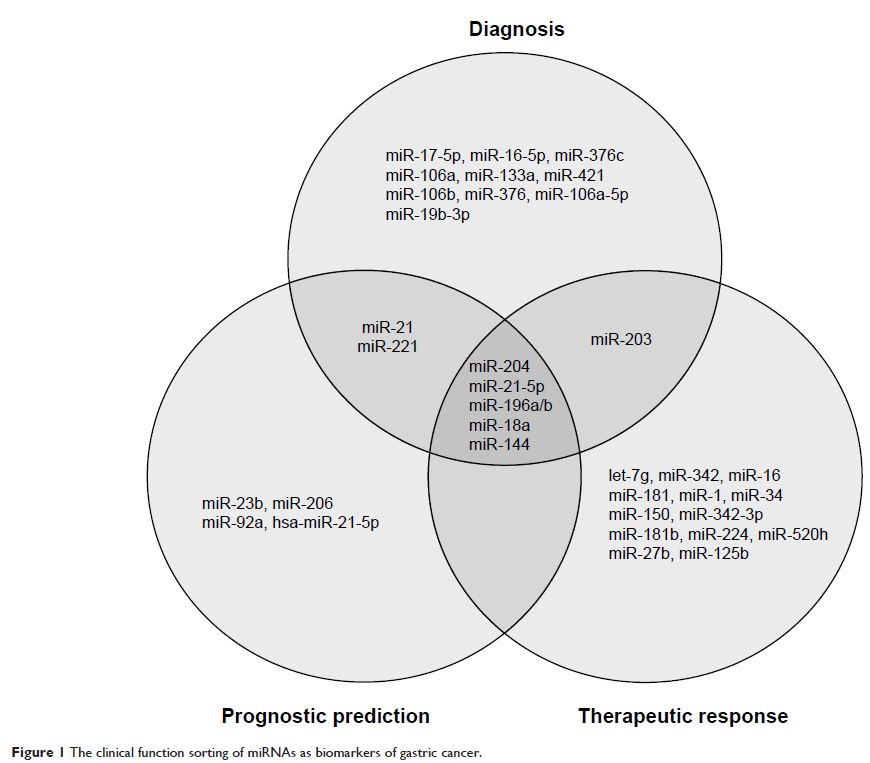
微小 RNA 作为胃癌诊断、治疗和预后的潜在生物标志物
Authors Yuan HL, Wang T, Zhang KH
Received 13 November 2017
Accepted for publication 9 May 2018
Published 6 July 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 3891—3900
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S156921
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Andrew Yee
Peer reviewer comments 4
Editor who approved publication: Dr Faris Farassati
Abstract: Despite the widespread use of
endoscopy and conventional tumor biomarkers, gastric cancer (GC) remains one of
the most frequent causes of cancer-related deaths worldwide due to its late
diagnosis and poor response to treatment. Valuable and practical biomarkers are
urgently needed to screen patients with a high risk of GC that can complement
endoscopic diagnosis. Such biomarkers will enable the efficient prediction of
therapeutic response and prognosis of GC patients and favor the establishment
of an effective treatment strategy for each and every patient. MicroRNAs (miRNAs)
are a class of small non-coding RNA sequences that play important roles in
modulating key biological processes by regulating the expression of target
genes. Expectedly, miRNAs are abnormally expressed within the tumor tissue and
in associated biological fluids of GC patients including their blood, gastric
juice, and urine. Accumulating evidence indicates that miRNAs are potential
biomarkers with multiple diagnostic functions for GC. Here, we review recent
advances and challenges in using miRNAs, particularly biofluid miRNAs, as GC
biomarkers with potential clinical applications including diagnosing,
clinically staging, and predicting malignant behaviors, therapy response,
recurrence after surgery and survival time.
Keywords: gastric cancer,
microRNA, biomarker, diagnosis, prognosis