9 0 8 0 2
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 2.6 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.9 Clin Epidemiol
- 3.3 Cancer Manag Res
- 3.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.6 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.8 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.8 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 8.0 Int J Nanomed
- 2.3 Int J Women's Health
- 3.2 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 4.0 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.2 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.8 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.7 J Pain Res
- 3.3 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 4.3 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.9 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 3.5 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.5 J Inflamm Res
- 2.3 Int J Gen Med
- 4.1 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.2 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.3 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 3.3 J Multidiscip Healthc

消退介质 maresin 1 可改善有神经性疼痛的脊神经结扎模型大鼠的疼痛超敏反应
Authors Gao J, Tang C, Tai LW, Ouyang Y, Li N, Hu Z, Chen X
Received 24 December 2017
Accepted for publication 21 May 2018
Published 10 August 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 1511—1519
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/JPR.S160779
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Andrew Yee
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Erica Wegrzyn
Background: Pro-resolving mediators (PRMs) are considered as emerging
analgesics for chronic pain. Maresin 1 (MaR1) is a newly identified member of
PRMs, and recent studies implicate its potential role in some pain conditions.
As the function of MaR1 in neuropathic pain remains unclear, we investigated
the effects of MaR1 on pain hypersensitivity and the underlying mechanism using
a rat spinal nerve ligation (SNL) model of neuropathic pain.
Materials and
methods: MaR1 (100 ng/10 μL) or commensurable
artificial cerebrospinal fluid was delivered via intrathecal catheter from days
3 to 5 post-SNL followed by assessment of mechanical allodynia and thermal
hyperalgesia. Ipsilateral L4–L5 spinal cord tissue was collected on day 7
post-SNL and assessed by Western blotting, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay or
immunohistochemistry.
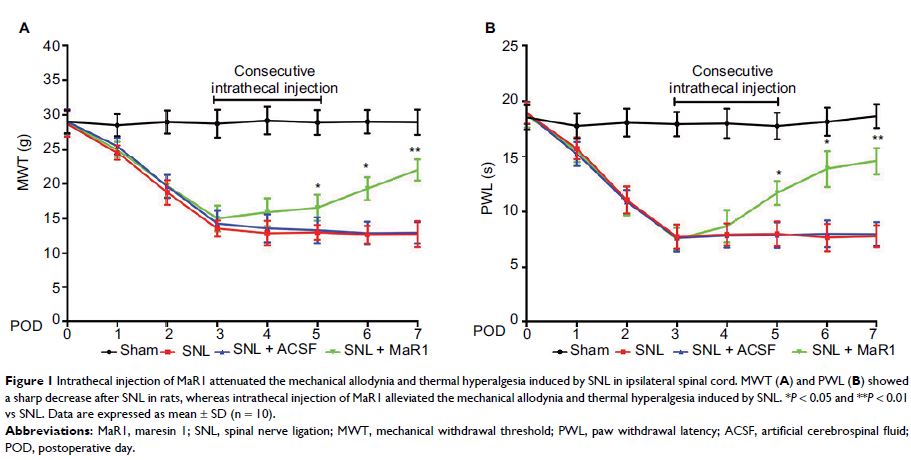
Results: Intrathecal MaR1 significantly attenuated mechanical allodynia and
thermal hyperalgesia from day 5 to day 7 post-SNL, which was associated with
decreased spinal levels of glial markers, GFAP and IBA1. It was also found that
intrathecal MaR1 downregulated phosphorylation levels of NF-κB p65 and its
nuclear translocation, as well as decreased protein levels of pro-inflammatory
cytokines, TNF-α, IL-1β and IL-6. Further, MaR1 treatment restored PSD95 and
synapsin II levels, suggesting that MarR1 also protected synaptic integrity.
Conclusion: Our results indicate that MaR1 ameliorates the SNL-induced
neuropathic pain by regulating glial activities and pro-inflammatory cytokines
release. The present study offers insight into the potential of MaR1 as a novel
intervention to ameliorate neuropathic pain.
Keywords: maresin 1, neuropathic pain, spinal nerve ligation, inflammation,
NF-κB p65