9 0 8 0 2
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 2.6 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.9 Clin Epidemiol
- 3.3 Cancer Manag Res
- 3.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.6 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.8 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.8 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 8.0 Int J Nanomed
- 2.3 Int J Women's Health
- 3.2 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 4.0 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.2 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.8 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.7 J Pain Res
- 3.3 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 4.3 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.9 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 3.5 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.5 J Inflamm Res
- 2.3 Int J Gen Med
- 4.1 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.2 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.3 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 3.3 J Multidiscip Healthc

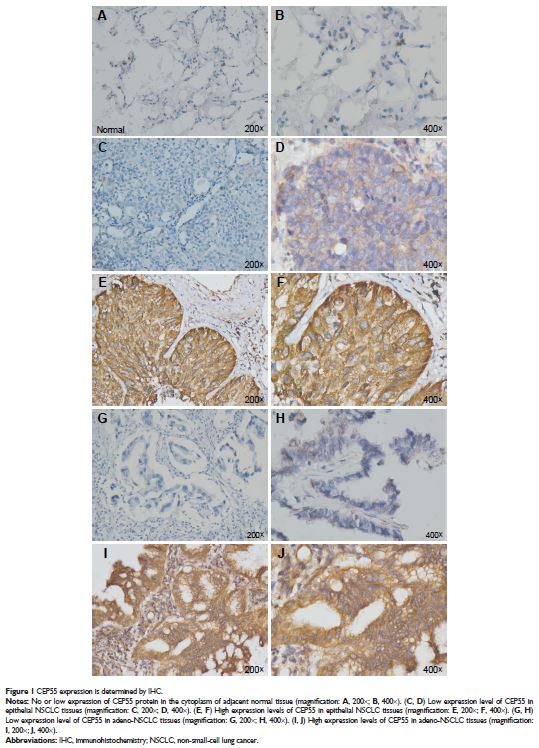
高 CEP55 表达与非小细胞肺癌的不良预后相关
Authors Jiang C, Zhang Y, Li Y, Lu J, Huang Q, Xu R, Feng Y, Yan S
Received 16 February 2018
Accepted for publication 2 May 2018
Published 17 August 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 4979—4990
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S165750
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Andrew Yee
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr XuYu Yang
Objectives: Lung cancer is the most common and lethal malignancy worldwide. CEP55 was found to be overexpressed in multiple types of cancer. However, the expression pattern of CEP55 and its clinical significance in non-small-cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC) have not been investigated by immunohistochemistry.
Materials and methods: In this study, we analyzed 203 primary NSCLC specimens from Sun Yat-Sen University Cancer Center to investigate the clinical role of CEP55 in lung cancer. Tissue microarray was successfully generated for immunohistochemical evaluation. The correlation between CEP55 expression and clinical characteristics and survival was analyzed statistically. The predictive effect of CEP55 and APOBEC3B (AP3B) coexpression in lung cancer patients’ prognosis was evaluated.
Results: We found that the CEP55 expression was commonly elevated in NSCLC tissues and overexpression of CEP55 was correlated with unfavorable prognosis in the patients with NSCLC. Furthermore, the combination of CEP55 and AP3B expression was significantly predictive of clinical outcome in all NSCLC patients.
Conclusion: CEP55 may act as a useful and novel prognostic biomarker for NSCLC. Further studies into the mechanism of CEP55 are warranted.
Keywords: CEP55, non-small-cell lung cancer, immunohistochemistry, prognosis