9 0 8 1 0
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 2.6 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.9 Clin Epidemiol
- 3.3 Cancer Manag Res
- 3.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.6 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.8 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.8 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 8.0 Int J Nanomed
- 2.3 Int J Women's Health
- 3.2 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 4.0 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.2 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.8 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.7 J Pain Res
- 3.3 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 4.3 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.9 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 3.5 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.5 J Inflamm Res
- 2.3 Int J Gen Med
- 4.1 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.2 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.3 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 3.3 J Multidiscip Healthc

miR-517a 通过直接靶向 FBP1 促进 HCC 中的 Warburg 效应
Authors Zhang D, Li Z, Li T, Luo D, Feng X, Liu Y, Huang J
Received 24 April 2018
Accepted for publication 9 August 2018
Published 13 November 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 8025—8032
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S172084
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Giandomenico Roviello
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Jianmin Xu
Purpose: Hepatocellular
carcinoma (HCC) is one of the most aggressive malignancies worldwide. Our aim
is to explore the expression and biological function of miR-517a in HCC.
Materials and methods: We
performed qRT-PCR to detect the expression of miR-517a in clinical samples and
cell lines. CKK-8 assay and colony formation assay were employed to detect the
miR-517a regulated cell proliferation. Glucose uptake and lactate production
were examined to determine the Warburg effect. We also performed ECAR assay
using Seahorse system. Luciferase acitivy assay was used to examine the binding
of FBP1 3’UTR by miR-517a.
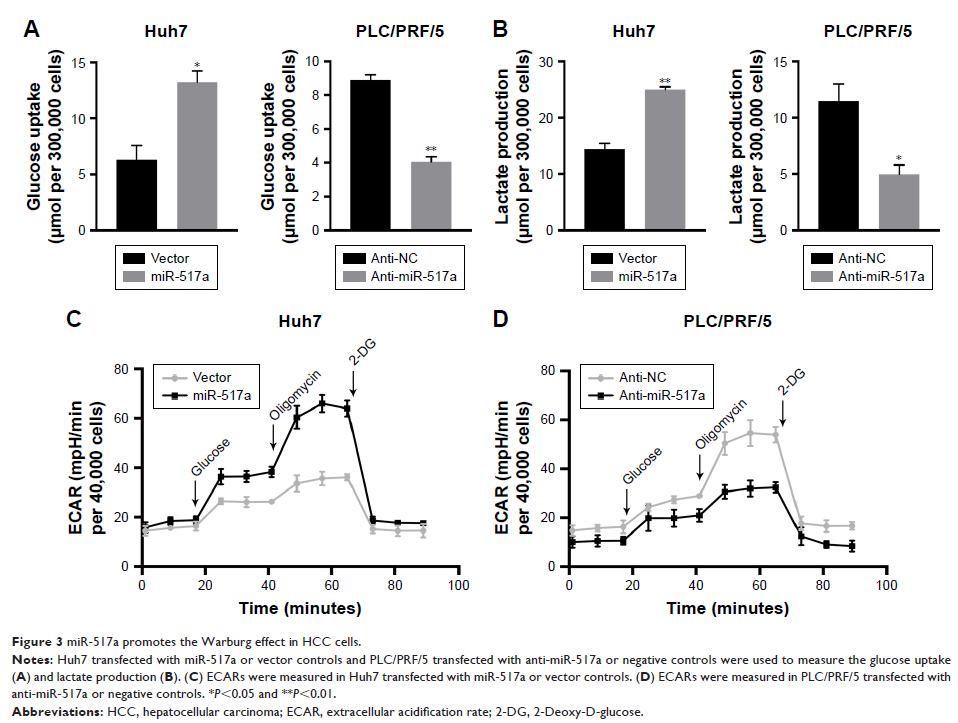
Results: miR-517a
was upregulated in HCC samples in both genomic and mRNA levels. Moreover,
overexpression of miR-517a promoted cell proliferation and Warburg effect.
Mechanically, miR-517a could directly target the 3′-UTR of FBP1. In addition,
restoring the expression of FBP1 inhibited cell growth.
Conclusion: We
demonstrated that miR-517a acts as an oncogene to promote Warburg effect in
HCC, favoring tumor growth, and miR-517a/FBP1 could be a novel target for HCC treatment.
Keywords: miR-517a,
HCC, FBP1, Warburg effect