9 1 2 3 6
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 2.6 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.9 Clin Epidemiol
- 3.3 Cancer Manag Res
- 3.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.6 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.8 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.8 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 8.0 Int J Nanomed
- 2.3 Int J Women's Health
- 3.2 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 4.0 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.2 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.8 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.7 J Pain Res
- 3.3 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 4.3 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.9 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 3.5 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.5 J Inflamm Res
- 2.3 Int J Gen Med
- 4.1 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.2 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.3 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 3.3 J Multidiscip Healthc

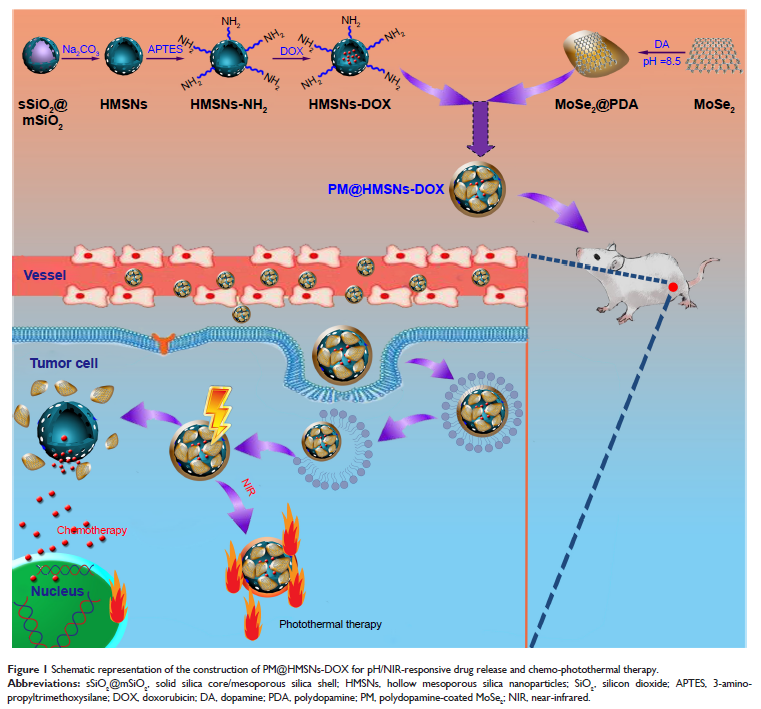
制备聚多巴胺包覆的 MoSe2 包裹的中空介孔二氧化硅纳米平台,用于药物控释和化学光热疗法
Authors Chai S, Kan S, Sun R, Zhou R, Sun Y, Chen W, Yu B
Received 27 July 2018
Accepted for publication 22 October 2018
Published 16 November 2018 Volume 2018:13 Pages 7607—7621
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S181681
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Govarthanan Muthusamy
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
Background: Integration
of several types of therapeutic agents into one nanoplatform to enhance
treatment efficacy is being more widely used for cancer therapy.
Methods: Herein, a
biocompatible polydopamine (PDA)-coated MoSe2-wrapped
doxorubicin (DOX)-loaded hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticles (HMSNs)
nanoplatform (PM@HMSNs-DOX) was fabricated for dual-sensitive drug release and
chemo-photothermal therapy for enhancing the therapeutic effects on breast
cancer. The HMSNs were obtained by a “structural difference-based selective
etching” strategy and served as the drug carrier, exhibiting a high DOX loading
capacity of 427 mg/g HMSNs-NH2, and then wrapped with PDA-coated MoSe2 layer to
form PM@HMSNs-DOX. Various techniques proved the successful fabrication of the
nanocomposites.
Results: The
formed PM@HMSNs-DOX nanocomposites exhibited good biocompatibility, good
stability, and super-additive photothermal conversion efficiency due to the
cooperation of MoSe2 and PDA. Simultaneously, the
pH/near-infrared-responsive drug release profile was observed, which could
enhance the synergistic therapeutic anticancer effect. The antitumor effects of
PM@HMSNs-DOX were evaluated both in vitro and in vivo, demonstrating
that the synergistic therapeutic efficacy was significantly superior to any
monotherapy. Also, in vivo pharmacokinetics studies showed that
PM@HMSNs-DOX had a much longer circulation time than free DOX. In addition,
in vitro and in vivo toxicity studies certified that PM@HMSNs are
suitable as biocompatible agents.
Conclusion: Our
nanoplatform loaded with DOX displays pH/near-infrared-induced chemotherapy and
excellent photothermal therapy, which hold great potential for cancer
treatment.
Keywords: hollow
mesoporous silica nanoparticles, MoSe2, polydopamine,
chemo-photothermal therapy