9 1 2 3 6
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 2.6 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.9 Clin Epidemiol
- 3.3 Cancer Manag Res
- 3.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.6 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.8 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.8 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 8.0 Int J Nanomed
- 2.3 Int J Women's Health
- 3.2 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 4.0 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.2 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.8 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.7 J Pain Res
- 3.3 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 4.3 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.9 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 3.5 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.5 J Inflamm Res
- 2.3 Int J Gen Med
- 4.1 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.2 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.3 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 3.3 J Multidiscip Healthc

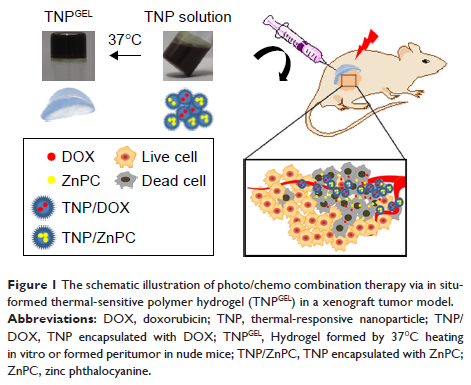
通过将 DOX 和 ZnPC 封装到原位成型的热敏聚合物水凝胶中可提高光/化学治疗组合治疗膀胱肿瘤的效率
Authors Huang Z, Xiao H, Lu X, Yan W, Ji Z
Received 5 July 2018
Accepted for publication 9 October 2018
Published 19 November 2018 Volume 2018:13 Pages 7623—7631
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S179226
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Govarthanan Muthusamy
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
Background: Chemotherapy after transurethral
resection is commonly recommended for bladder cancer. However, studies have
shown that chemotherapy solely can hardly decrease progression rates of bladder
cancer. The combination of chemotherapeutic agents with photodynamic therapy
(PDT), a new promising localized therapy, may become a workable strategy for
combating bladder cancer. This study reports the combination of doxorubicin
(DOX)-based chemotherapy and zinc phthalocyanine (ZnPC)-based PDT using in
situ-formed thermal-responsive copolymer hydrogel.
Materials and methods: The copolymer was synthesized by polymerization of 3-caprolactone,
1,4,8-trioxa[4.6]spiro-9-undecanone and poly(ethylene glycol) and was
abbreviated as PCL-PTSUO-PEG. The thermal-responsive nanoparticles (TNPs) were
prepared by the nanoprecipitation technology. The thermal-responsive hydrogel
was formed after 37°C heating of TNP solution. The size, morphology and dynamic
viscosity of hydrogel were detected. The in vitro drug release profile of
TNP/DOX/ZnPC was performed. Cell uptake, cell inhibition and ROS generation of
TNP/DOX/ZnPC were studied in 5637 cells. The in vivo antitumor activity of
TNP/DOX/ZnPC was evaluated in nude mice bearing 5637 cells xenograft.
Results: TNP/DOX
and TNP/ZnPC had an average diameter of 102 and 108 nm, respectively.
After being heated at 37°C for 5 minutes, TNP/DOX and TNP/ZnPC solution
turned uniform light red and dark green hydrogel. ZnPC encapsulation designed
by TNP could significantly improve its aqueous solubility to 1.9 mg/mL.
Cell inhibition showed that the best cell inhibition was found, with cell
viability of 18.5%, when the weight ratio of DOX and ZnPC encapsulated in the
TNP reached about 1:5. TNP/DOX/ZnPC generated relative high level of ROS with
4.8-fold of free ZnPC and 1.6-fold of TNP/ZnPC. TNP/DOX/ZnPC showed only 8-fold
of relative tumor growth without obvious toxicity to the mice.
Conclusion: Thermosensitive
thermal-responsive hydrogel reported in this contribution are promising in
situ-formed matrix for DOX- and ZnPC-based photo/chemo combination treatment
for bladder cancer therapy.
Keywords: chemotherapy,
photodynamic therapy, combination therapy, hydrogel, thermo-sensitive, bladder
cancer