9 1 1 5 0
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 2.6 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.9 Clin Epidemiol
- 3.3 Cancer Manag Res
- 3.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.6 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.8 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.8 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 8.0 Int J Nanomed
- 2.3 Int J Women's Health
- 3.2 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 4.0 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.2 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.8 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.7 J Pain Res
- 3.3 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 4.3 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.9 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 3.5 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.5 J Inflamm Res
- 2.3 Int J Gen Med
- 4.1 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.2 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.3 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 3.3 J Multidiscip Healthc

lncRNA CASC9 通过靶向 miR-125a-3p/Nrg1 调节血管瘤内皮细胞的细胞迁移和侵袭
Authors Li X, Chen B, Chi D, Zhang Y, Jiang W
Received 30 July 2018
Accepted for publication 4 September 2018
Published 7 January 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 423—432
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S181914
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Amy Norman
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr William Cho
Background: Despite
being one of the most common benign tumors, the prevalence and pathogenesis of
hemangiomas (HAs) are poorly understood. We aimed to identify the biological
role of the long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) CASC9 in the HA-derived endothelial
cell (HDECs) phenotype as well as elucidate the mechanism involved.
Methods: The
expression of CASC9 was identified by reverse transcription-quantitative
polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR). the effect of CASC9 on cell proliferation,
migration and invasion of HDECs were examined by CCK8, wound healing, and
transwell assay, respectively. Bioinformatics analysis and a luciferase
reporter assay were utilized to investigated the mechanisms involved. The in
vivo tumorigenesis capability of CASC9 on HA was also evaluated.
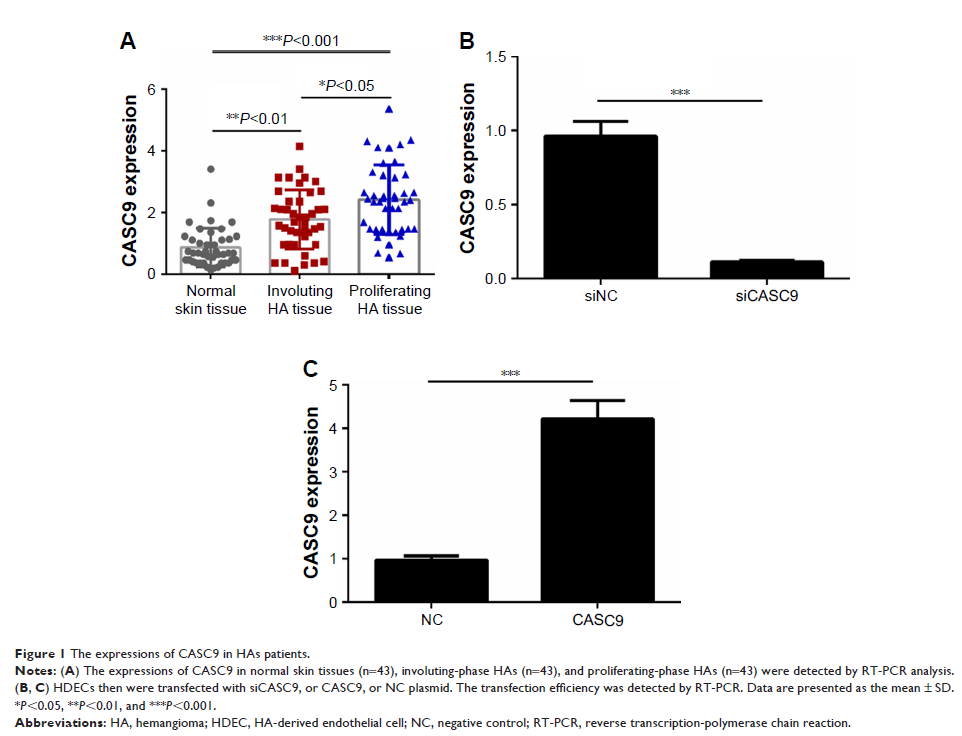
Results: The
expression of CASC9 was significantly elevated in HA tissue compared to normal
tissue. Down-regulation of CASC9 inhibited proliferation, migration, and
invasion of HDECs. The translation of cyclinD1, N-cadherin, Twist, and MMP2 was
also decreased by CASC9 knockdown treatment. Furthermore, CASC9 over-expression
exerted the opposite effect of proliferation, migration, and invasion of HDECs.
We also found that CASC9 interacts with miR-125a-3p/Nrg1 to regulate cellular
functions. Interestingly, miR-125a-3p can reverse the effect of CASC9 on
proliferation, migration, and invasion of HDECs. Together, the clinical data
showed that CASC9 expression is negatively correlated with miR-125a-3p
expression and positively correlated with Nrg1 expression. CASC9 also exerted
anti-tumorigenesis capability in vivo.
Conclusion: Our study
indicates that CASC9 accelerates cell growth and invasion of HDECs and provides
new insights for the diagnosis and molecular therapy of HA.
Keywords: CASC9,
cell migration, invasion, hemangioma, miR-125a-3p, Nrg1