9 1 1 5 0
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 2.6 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.9 Clin Epidemiol
- 3.3 Cancer Manag Res
- 3.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.6 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.8 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.8 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 8.0 Int J Nanomed
- 2.3 Int J Women's Health
- 3.2 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 4.0 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.2 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.8 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.7 J Pain Res
- 3.3 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 4.3 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.9 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 3.5 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.5 J Inflamm Res
- 2.3 Int J Gen Med
- 4.1 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.2 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.3 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 3.3 J Multidiscip Healthc

包覆喜树碱的聚乳酸羟基乙酸共聚物纳米粒对体外细胞色素 P450 活性的影响
Authors Bao H, Zhang Q, Yan Z
Received 27 September 2018
Accepted for publication 11 December 2018
Published 7 January 2019 Volume 2019:14 Pages 383—391
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S188984
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
Background: Poly(lactic-co -glycolic acid)
(PLGA) has emerged as a promising anticancer drug delivery scaffold.
Camptothecin (CPT) has been fabricated into a variety of nano-sized
formulations to improve drug action. We report an experimental study on the
effect of CPT-encapsulated PLGA (PLGA-CPT) nanoparticles (NPs) on
drug-metabolizing cytochrome P450 enzyme, CYP3A4.
Materials and methods: PLGA-CPT
NPs were prepared by a single emulsion–solvent evaporation method.
Results: Transmission
electron micrography showed that the NPs had a round and regular shape with a
mean diameter of 94.6±5.7 nm. An in vitro drug release study showed that
CPT was continuously released for 48 h. PLGA-CPT NPs showed greater cytotoxic
effects on the HepG2 cell line compared with an equal dose of free CPT.
Correlation with 4-h uptake data suggested that this was due to a higher
cellular uptake amount of CPT from PLGA-CPT NPs than from free CPT. PLGA-CPT
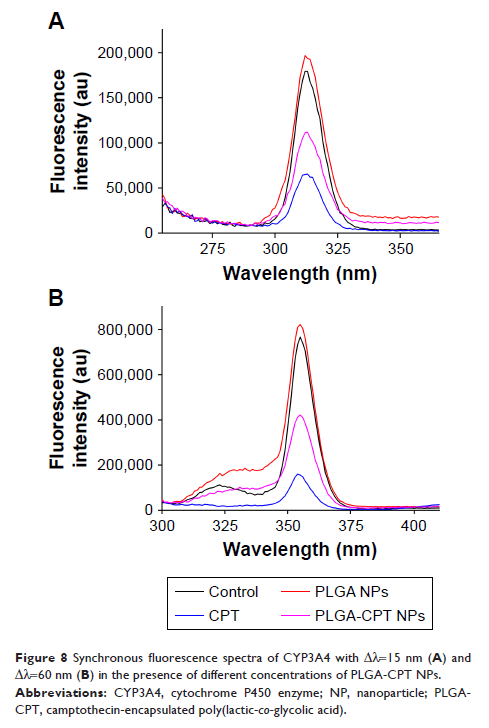
NPs tended to inhibit CYP3A4 activity isolated from HepG2 cells. However,
PLGA-CPT NPs had no effect on the CYP3A4 mRNA levels. Furthermore, the
interaction between PLGA-CPT NPs and CYP3A4 was investigated by
ultraviolet–visible absorption spectroscopy and fluorescence spectroscopy.
Conclusion: Taken
together, the results demonstrate that CYP3A4 may be inhibited by PLGA-CPT NPs
and interference with biotransformation should be considered when using NPs as drug
delivery vesicles.
Keywords: camptothecin,
cytochrome P450, nanoparticle, drug delivery