108384
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

对结核病患者参与医疗保健的看法:一项定性研究
Authors Ren J, Li QL, Zhang TH, Li XM, Zhang SR, Wright JJ, Liu HN, Hua ZQ
Received 25 October 2018
Accepted for publication 8 December 2018
Published 11 January 2019 Volume 2019:13 Pages 107—117
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/PPA.S191800
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Naifeng Liu
Purpose: Adherence
to treatment is cited as a key challenge in fighting tuberculosis (TB).
Treatment of TB requires patients to actively engage in their care. The purpose
of this study was to explore the perceptions of patients with TB regarding
their engagement in health care.
Patients and methods: The study
was conducted in three medical wards in one hospital. Purposive sampling was
used to recruit participants. Semi-structured, audiotaped interviews were
conducted and analyzed using thematic analysis.
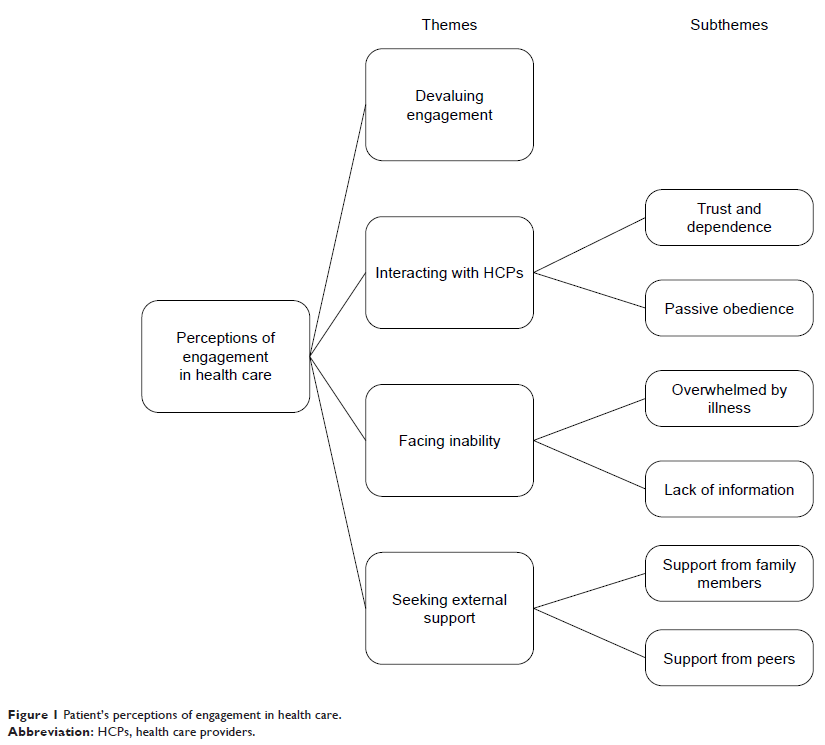
Results: Twenty-three
patients participated in the study. Four major themes emerged: 1) devaluing
engagement; 2) interacting with health care providers (HCPs); 3) facing
inability; and 4) seeking external support.
Conclusion: The
patients’ perceptions of their engagement in health care were generally
negative. Paying attention to the preferences and needs of patients and making
decisions accordingly are effective strategies for promoting patient
engagement. Moreover, HCPs should be aware of their crucial role in helping
patients make sense of what engagement is and how to engage. In the process of
engagement, providers should establish effective interactions with patients and
cooperate with family and peers.
Keywords: tuberculosis,
patient engagement, qualitative study, treatment adherence