108384
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

我们应该为接受治疗性肝切除术的微血管浸润的肝细胞癌患者使用索拉非尼吗?
Authors Huang Y, Zhang Z, Zhou Y, Yang J, Hu K, Wang Z
Received 12 September 2018
Accepted for publication 4 December 2018
Published 11 January 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 541—548
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S187357
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Amy Norman
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Tohru Yamada
Objective: Microvascular
invasion (MVI) has been proved to be an independent risk factor for the
recurrence of HCC. If promptly treated, the recurrence rate can be reduced and
the total survival time can be prolonged. The aim of this study is to analyze
the effect of sorafenib on the clinical outcomes in HCC patients with MVI after
curative hepatectomy.
Methods: HCC
patients who underwent hepatectomy and were pathologically diagnosed with MVI
were retrospectively analyzed. Patients were divided into sorafenib group and
control group. Sorafenib 400 mg, twice daily, was administered orally after
surgery in the sorafenib group. The recurrence-free survival (RFS) and overall
survival (OS) were observed during follow-up, and associated factors were
analyzed using univariate and multivariate COX regression.
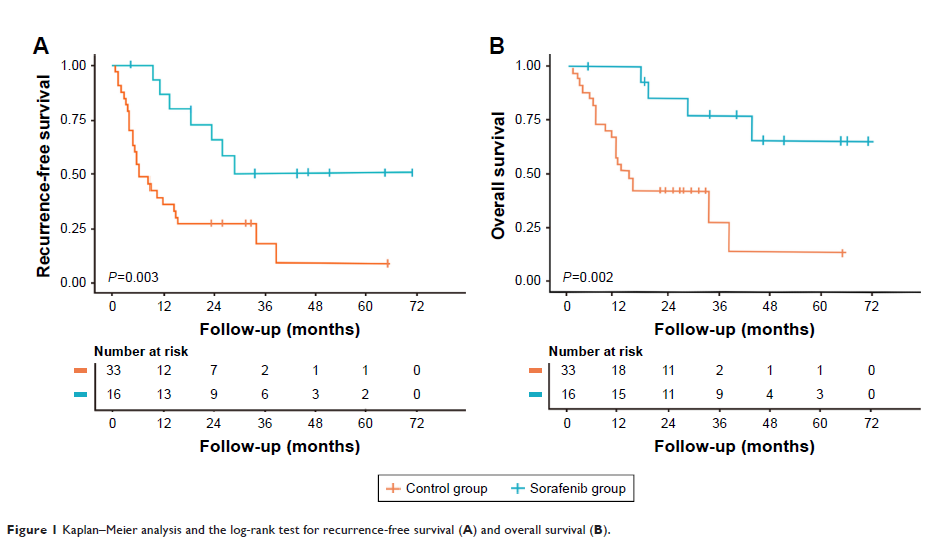
Results: There was
no significant difference in demographics, clinical staging, and tumor index
between sorafenib group (16 patients) and control group (33 matched patients).
The RFS and OS were both longer in the sorafenib group, and the 3-years RFS
rates of the sorafenib group and control group were 56.3% (9 of 16) and 24.2%
(8 of 33), respectively (P =0.027). The 3-year OS rate of the sorafenib group
was 81.3% (13 of 16), which was significantly higher than that of the control
group (39.4%, P =0.006). The results of multivariate COX regression
indicated that treatment with sorafenib was an independent associated factor
for RFS and OS.
Conclusion: We
believe that using sorafenib therapy after curative hepatectomy in HCC patients
with MVI is effective and beneficial as it can reduce recurrence and prolong
the survival time.
Keywords: sorafenib,
hepatocellular carcinoma, microvascular invasion, hepatectomy, survival rate