9 0 8 1 0
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 2.6 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.9 Clin Epidemiol
- 3.3 Cancer Manag Res
- 3.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.6 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.8 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.8 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 8.0 Int J Nanomed
- 2.3 Int J Women's Health
- 3.2 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 4.0 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.2 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.8 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.7 J Pain Res
- 3.3 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 4.3 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.9 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 3.5 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.5 J Inflamm Res
- 2.3 Int J Gen Med
- 4.1 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.2 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.3 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 3.3 J Multidiscip Healthc

microRNA-877 通过直接靶向 MTDH 和调节 PTEN/Akt 通路抑制结直肠癌的恶性进展
Authors Zhang L, Li C, Cao L, Li H, Zou H, Li H, Pei H
Received 9 November 2018
Accepted for publication 15 February 2019
Published 8 April 2019 Volume 2019:11 Pages 2769—2781
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S194073
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Andrew Yee
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Ahmet Emre Eskazan
Background: Recently,
microRNA-877-5p (miR-877) was recognized as a cancer-associated miRNA in hepatocellular
and renal cell carcinomas. However, little is known regarding its expression
pattern and role in colorectal cancer (CRC) tumorigenesis.
Material and methods: In the
present study, reverse-transcription quantitative polymerase chain reaction was
performed to detect miR-877 expression in CRC tissues and cell lines. A series
of functional experiments were used to determine the effects of miR-877
upregulation on CRC cell proliferation, colony formation, apoptosis, migration,
and invasion. In addition, the regulatory role of miR-877 in tumor growth was
examined in vivo using a xenograft experiment. More importantly, the mechanisms
underlying the action of miR-877 in CRC were explored.
Results: A
significant decrease in the expression of miR-877 was observed in CRC tissues
and cell lines. Low miR-877 expression correlated with lymph node metastasis
and TNM stage of CRC patients. Functional experiments revealed that ectopic
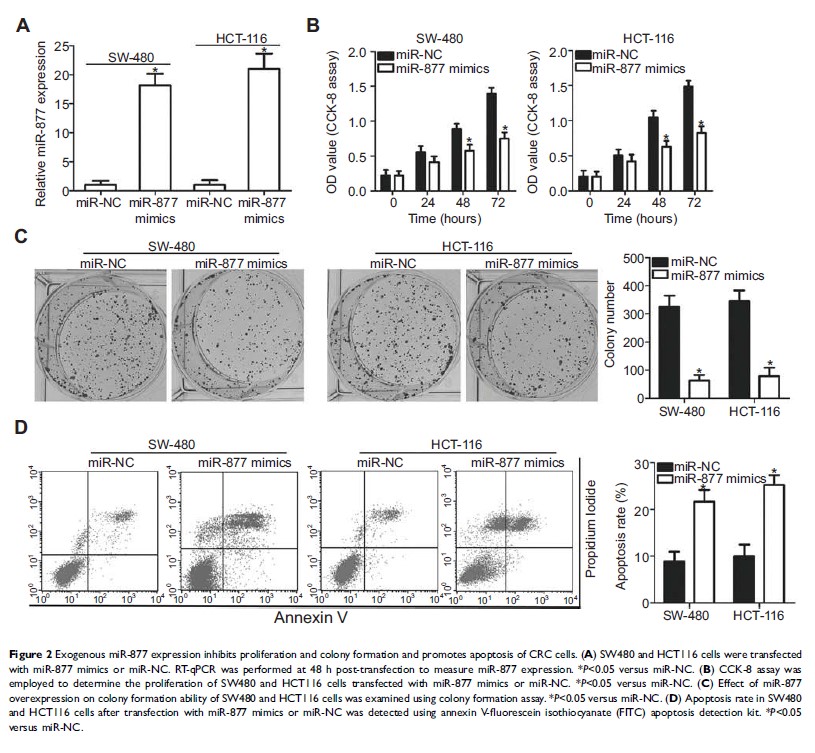
expression of miR-877 suppressed CRC cell proliferation and colony formation ability,
induced cell apoptosis, inhibited cell migration and invasion in vitro, and
reduced tumor growth in vivo. Metadherin (MTDH ) was recognized as a direct target of miR-877 in
CRC cells. It was notably overexpressed in CRC tissues, and its expression was
inversely correlated with that of miR-877 expression. Furthermore, MTDH knockdown
simulated the tumor suppressor activity of miR-877 in CRC cells. MTDH restoration
impaired the suppressive effects of miR-877 on malignant phenotypes of CRC
cells. In addition, miR-877 inhibited the activation of the PTEN/Akt signaling
pathway by regulating MTDH expression both in vitro and in vivo.
Conclusion: Collectively,
these results demonstrate that miR-877 inhibits the progression of CRC, at
least partly by the direct targeting of MTDH and regulation of the PTEN/Akt pathway.
Thus, miR-877 may serve as a potential therapeutic target for the treatment of
patients with CRC.
Keywords: microRNA-877,
colorectal cancer, metadherin, PTEN/Akt pathway