9 0 9 6 8
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 2.6 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.9 Clin Epidemiol
- 3.3 Cancer Manag Res
- 3.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.6 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.8 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.8 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 8.0 Int J Nanomed
- 2.3 Int J Women's Health
- 3.2 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 4.0 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.2 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.8 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.7 J Pain Res
- 3.3 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 4.3 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.9 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 3.5 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.5 J Inflamm Res
- 2.3 Int J Gen Med
- 4.1 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.2 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.3 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 3.3 J Multidiscip Healthc

高 CD3D/CD4 比率预示肌肉浸润性膀胱癌的较高存活率
Authors Shi MJ, Meng XY, Wu QJ, Zhou XH
Received 16 October 2018
Accepted for publication 7 February 2019
Published 12 April 2019 Volume 2019:11 Pages 2987—2995
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S191105
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristina Weinberg
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Professor Nakshatri
Background: Bladder
cancer is a common malignancy that affects the human urinary tract.
Muscle-invasive bladder cancer (MIBC) is aggressive and has poor prognosis.
Previous studies have reported that the tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs)
were associated with MIBC outcome; however, inconsistency remains and mRNA
level TIL markers’ prognostic significance in MIBC is unclear.
Materials and methods: In the
present study, we reanalyzed data from four public datasets (the Cancer Genome
Atlas for investigation; and CIT, GSE5287, and GSE31684 for validation) to
examine the prognostic significance of CD3D, CD4, CD8A, CD3D/CD4 and CD3D/CD8A
in MIBC.
Results: We found that
the CD3D/CD4 ratio was a stable independent prognostic factor in MIBC (beta =
−0.87, P =
0.025); high CD3D/CD4 ratio predicted better survival in MIBC, and the power of
this association was much stronger in basal-squamous tumors (beta =
−4.73, P =
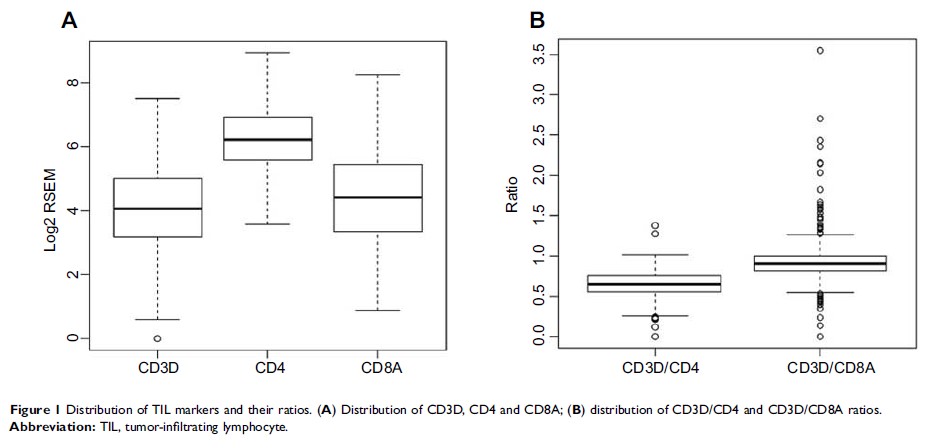
2.67E-06). We also noted that the CD4 expression was significantly higher than
CD3D (P <
0.05), indicating the presence of CD3−CD4+ cells
which could be immune-suppressing.
Conclusion: The
CD3D/CD4 ratio can be viewed as a prognostic marker and a rough measurement for
the interaction between immune-effecting CD3+ TILs and
immune-suppressing CD3−CD4+ cells in
MIBC, and this interaction may play a particularly important role in
anti-cancer immunity in basal-squamous tumors as it has a very strong
association with survival in this subtype, and may be used to select potential
responders to immunotherapy.
Keywords: bladder
cancer, muscle-invasive, tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes, CD3, CD4, CD8,
prognosis, immunotherapy, basal-squamous subtype