9 0 8 1 0
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 2.6 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.9 Clin Epidemiol
- 3.3 Cancer Manag Res
- 3.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.6 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.8 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.8 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 8.0 Int J Nanomed
- 2.3 Int J Women's Health
- 3.2 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 4.0 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.2 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.8 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.7 J Pain Res
- 3.3 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 4.3 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.9 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 3.5 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.5 J Inflamm Res
- 2.3 Int J Gen Med
- 4.1 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.2 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.3 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 3.3 J Multidiscip Healthc

液体抗溶剂沉淀:一种有效的叶黄素酯眼部靶向疗法
Authors Wu M, Feng Z, Deng Y, Zhong C, Liu Y, Liu J, Zhao X, Fu Y
Received 9 November 2018
Accepted for publication 12 February 2019
Published 15 April 2019 Volume 2019:14 Pages 2667—2681
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S194068
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Govarthanan Muthusamy
Peer reviewer comments 4
Editor who approved publication: Dr Mian Wang
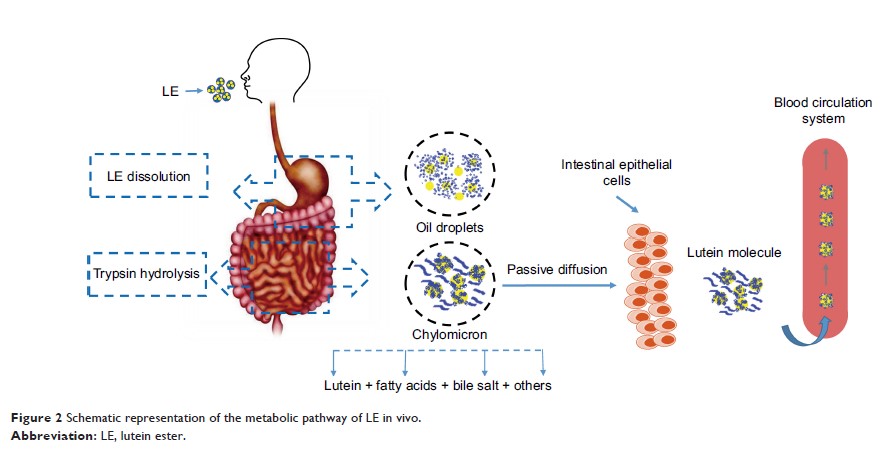
Background: Lutein
ester (LE) is an important carotenoid fatty acid ester. It is a form in which
lutein is present in nature and is produced by free non-esterification and
fatty acid esterification. LE is one of the safe sources of lutein. Increasing
lutein intake can prevent and treat age-related macular degeneration. In
addition, it can effectively inhibit gastric cancer, breast cancer, and
esophageal cancer. However, the poor aqueous solubility of LE has impeded its
clinical applications.
Objective: The
objective of this study was to prepare lutein ester nanoparticles (LE-NPs) by
liquid antisolvent precipitation techniques to improve the bioavailability of
LE in vivo and improve eye delivery efficiency.
Materials and methods: The
physical characterization of LE-NPs was performed, and their in vitro
dissolution rate, in vitro antioxidant capacity, in vivo bioavailability,
tissue distribution, and ocular pharmacokinetics were studied and evaluated.
Results: The LE
freeze-dried powder obtained under the optimal conditions possessed a particle
size of ~164.1±4.3 nm. The physical characterization analysis indicated the
amorphous form of LE-NPs. In addition, the solubility and dissolution rate of
LE-NPs in artificial gastric juice were 12.75 and 9.65 times that of the raw
LE, respectively. The bioavailability of LE-NPs increased by 1.41 times
compared with that of the raw LE. The antioxidant capacity of LE-NPs was also
superior to the raw LE. The concentration of lutein in the main organs of rats
treated with the LE-NPs was higher than that in rats treated with the raw LE.
The bioavailability of LE-NPs in rat eyeballs was found to be 2.34 times that
of the original drug.
Conclusion: LE-NPs
have potential application as a new oral pharmaceutical formulation and could
be a promising eye-targeted drug delivery system.
Keywords: solubility,
nanotechnology, drug delivery system, bioavailability, ocular pharmacokinetics