9 0 8 1 0
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 2.6 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.9 Clin Epidemiol
- 3.3 Cancer Manag Res
- 3.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.6 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.8 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.8 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 8.0 Int J Nanomed
- 2.3 Int J Women's Health
- 3.2 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 4.0 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.2 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.8 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.7 J Pain Res
- 3.3 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 4.3 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.9 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 3.5 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.5 J Inflamm Res
- 2.3 Int J Gen Med
- 4.1 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.2 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.3 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 3.3 J Multidiscip Healthc

单侧丘脑神经胶质瘤在休息状态下破坏人脑的大规模功能网络
Authors Li S, Gao L, Liu Y, Ao Y, Xu H
Received 2 September 2018
Accepted for publication 19 February 2019
Published 15 April 2019 Volume 2019:15 Pages 947—956
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/NDT.S186161
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Andrew Yee
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Jun Chen
Background: The
thalamus is an important deep brain structure for the synchronization of brain
rhythm and the integration of cortical activity. Human brain imaging and
computational modeling have non-invasively revealed its role in maintaining the
cortical network architecture and functional hierarchy.
Purpose: The
objective of this study was to identify the effect of unilateral thalamic
damage on the human brain intrinsic functional architecture.
Patients and methods: We
collected an 8-minute resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging
(R-fMRI) data on a 3.0 T magnetic resonance scanner for all the participants: a
preoperative patient with left thalamus destroyed by anaplastic astrocytoma
(WHO grade III type of astrocytoma) and 20 matched healthy controls. The R-fMRI
data was analyzed for functional connectivity and amplitude of spontaneous
fluctuations.
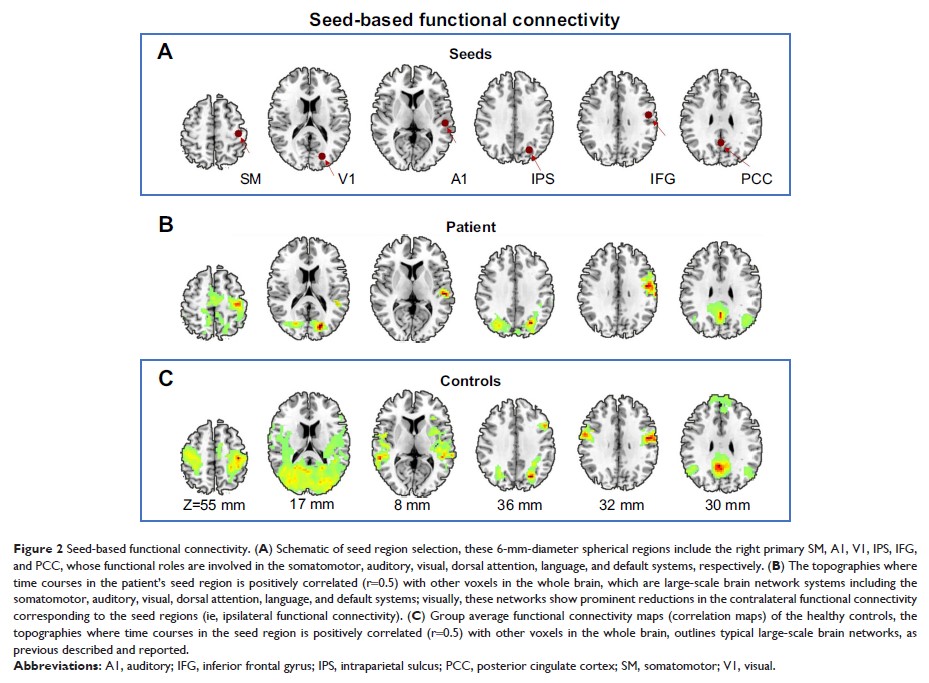
Results: The
patient showed prominent decrease in functional connectivity within primary
sensory networks and advanced cognitive networks, and extensive alterations in
between-network coupling. Further analysis of the amplitude of spontaneous
activity suggested significant decrease especially in the topographies of
default mode network and the Papez circuit.
Conclusion: This
result provided evidence about the consequences of thalamic destruction on the
correlation and landscape of spontaneous brain activity, promoting our
understanding of the effects of thalamic damage on large-scale brain networks.
Keywords: brain
networks, functional connectivity, default mode network, Papez circuit