9 0 7 9 9
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 2.6 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.9 Clin Epidemiol
- 3.3 Cancer Manag Res
- 3.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.6 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.8 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.8 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 8.0 Int J Nanomed
- 2.3 Int J Women's Health
- 3.2 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 4.0 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.2 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.8 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.7 J Pain Res
- 3.3 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 4.3 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.9 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 3.5 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.5 J Inflamm Res
- 2.3 Int J Gen Med
- 4.1 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.2 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.3 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 3.3 J Multidiscip Healthc

系统性炎症反应指数预测可切除的胰腺导管腺癌患者的存活和复发
Authors Li S, Xu H, Wang W, Gao H, Li H, Zhang S, Xu J, Zhang W, Xu S, Li T, Ni Q, Yu X, Wu C, Liu L
Received 12 December 2018
Accepted for publication 1 March 2019
Published 17 April 2019 Volume 2019:11 Pages 3327—3337
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S197911
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Ms Justinn Cochran
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Nakshatri
Purpose: The
systemic inflammation response index (SIRI), based on peripheral neutrophil,
monocyte, and lymphocyte counts, was recently emerged and used as a novel tool
in predicting prognosis in different types of cancer. Our aim was to
investigate the clinical significance of preoperative SIRI in patients with
resectable pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC).
Materials and methods: The SIRI
was developed in a training cohort of 371 PDAC patients undergoing radical
surgery between 2010 and 2013 and validated in a validation cohort of 310
patients from 2014 to 2015. Baseline clinicopathologic characteristics,
preoperative laboratory parameters and follow-up information were collected.
The optimal cutoff value of SIRI was determined by receiver operating
characteristic curve. Univariate and multivariate analysis were performed to
analyze the prognostic value of SIRI.
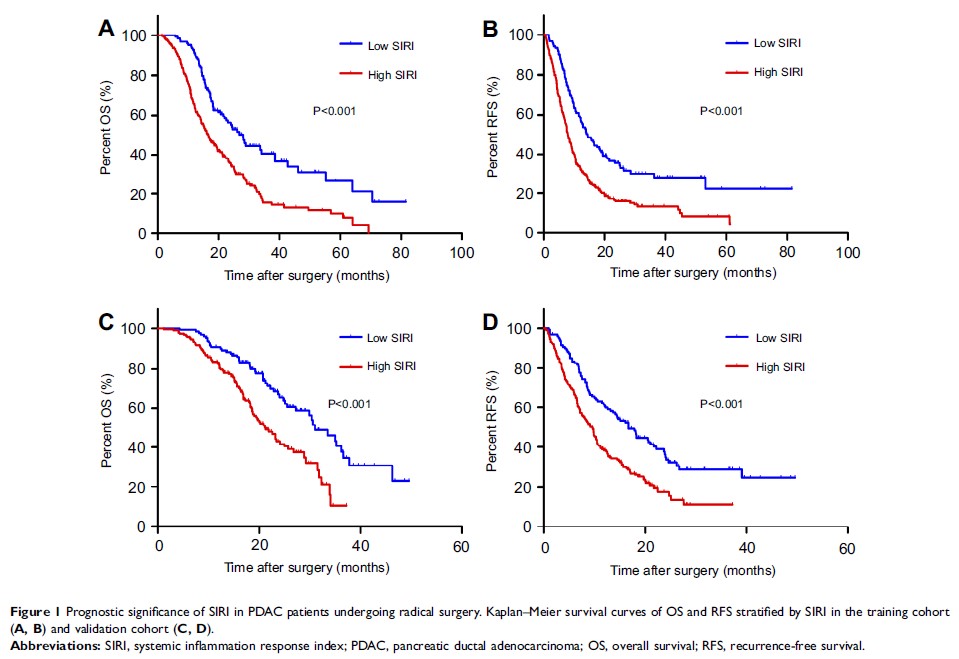
Results: The
optimal cutoff value of SIRI stratified patients into low SIRI group (≤0.69)
and high SIRI group (>0.69). Survival analysis showed that the median
overall survival (OS) and recurrence-free survival (RFS) were significantly
better in patients with low SIRI. The SIRI was an independent predictor of OS
and RFS in multivariate analysis. In addition, SIRI remained its prognostic
significance both in patients with early-stage diseases and in patients with
normal carbohydrate antigen 19-9 levels. High SIRI indicated poor treatment
response for patients who received postoperative adjuvant chemotherapy.
Conclusion: Preoperative
SIRI was an independent prognostic indicator of poor outcomes in PDAC patients
after radical resection. It might assist clinicians to identify high-risk
patients and choose the optimal individualized treatment strategy.
Keywords: pancreatic
ductal adenocarcinoma, systemic inflammation response index, overall survival,
recurrence-free survival, prognosis