9 0 8 0 2
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 2.6 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.9 Clin Epidemiol
- 3.3 Cancer Manag Res
- 3.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.6 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.8 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.8 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 8.0 Int J Nanomed
- 2.3 Int J Women's Health
- 3.2 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 4.0 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.2 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.8 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.7 J Pain Res
- 3.3 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 4.3 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.9 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 3.5 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.5 J Inflamm Res
- 2.3 Int J Gen Med
- 4.1 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.2 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.3 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 3.3 J Multidiscip Healthc

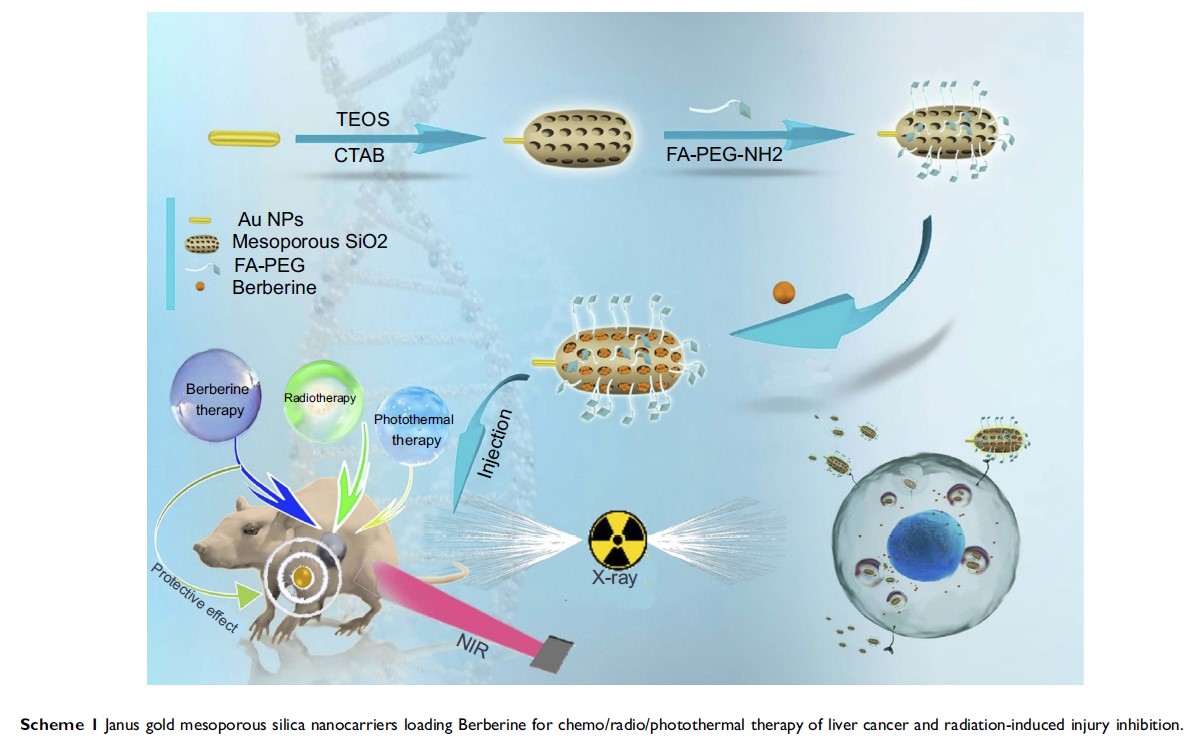
负载小檗碱的 Janus 型金介孔二氧化硅纳米载体用于肝癌的化疗/放射/光热治疗和放射诱导的损伤抑制
Authors Li XD, Wang Z, Wang XR, Shao D, Zhang X, Li L, Ge MF, Chang ZM, Dong WF
Received 20 February 2019
Accepted for publication 13 April 2019
Published 29 May 2019 Volume 2019:14 Pages 3967—3982
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S206044
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristina Weinberg
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
Background: The combination of chemotherapy with radiotherapy serves as a common therapeutic strategy in clinics. However, it is unsatisfactory due to its poor therapeutic efficiency and severe side-effects originating from chemotherapy-exerted systemic toxicity as well as radiation-induced injury.
Purpose: Hence, Berberine (Ber), an isoquinolin alkaloid with low toxicity and protective effects against radiotherapy, was used as a novel chemotherapeutic agent for chemo-radiotherapy of liver cancer.
Patients and methods: We preloaded Ber into folic acid targeting Janus gold mesoporous silica nanocarriers (FA-JGMSNs) for overcoming the poor bioavailability of Ber. Furthermore, FA-JGMSNs were not only employed as radiosensitizers for expanding radiotherapeutic effect, but also used as photothermal agents for supplementing chemo-radiotherapeutic effect by local photothermal therapy.
Results: In vitro and in vivo experiemtal results demonstrated the highly efficient anti-tumor effect, good biosafety as well as the effective protection of normal tissue of this nanoplatform.
Conclusion: Based on its superb performance, we believe our work provided a feasible strategy for triple-therapies of liver cancer.
Keywords: Berberine, chemotherapy, radio-sensitization, Au MSNs, Janus, photothermal therapy