9 0 9 6 8
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 2.6 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.9 Clin Epidemiol
- 3.3 Cancer Manag Res
- 3.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.6 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.8 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.8 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 8.0 Int J Nanomed
- 2.3 Int J Women's Health
- 3.2 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 4.0 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.2 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.8 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.7 J Pain Res
- 3.3 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 4.3 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.9 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 3.5 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.5 J Inflamm Res
- 2.3 Int J Gen Med
- 4.1 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.2 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.3 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 3.3 J Multidiscip Healthc

表皮生长因子受体酪氨酸激酶抑制剂用于治疗非小细胞肺癌的药物−药物相互作用比较研究
Authors Xu ZY, Li JL
Received 16 November 2018
Accepted for publication 12 March 2019
Published 9 July 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 5467—5484
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S194870
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristina Weinberg
Peer reviewer comments 4
Editor who approved publication: Prof. Dr. Geoffrey Pietersz
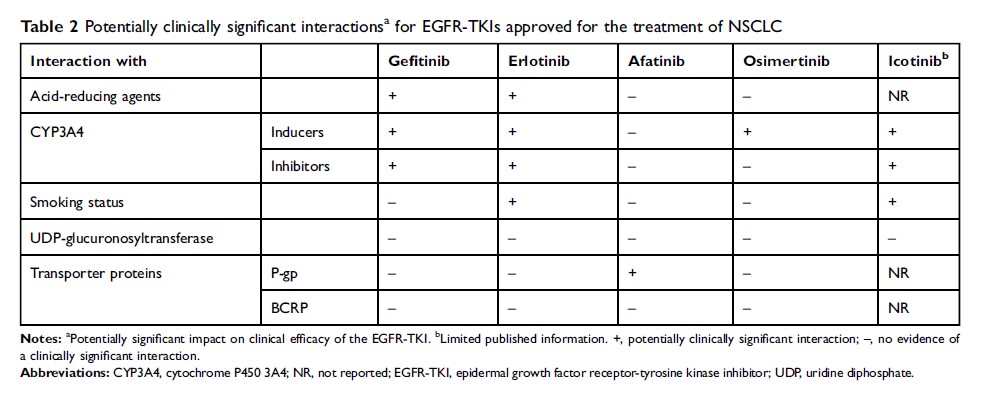
Abstract: The development of small-molecule tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) that target the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) has revolutionized the management of non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Because these drugs are commonly used in combination with other types of medication, the risk of clinically significant drug–drug interactions (DDIs) is an important consideration, especially for patients using multiple drugs for coexisting medical conditions. Clinicians need to be aware of the potential for clinically important DDIs when considering therapeutic options for individual patients. In this article, we describe the main mechanisms underlying DDIs with the EGFR-TKIs that are currently approved for the treatment of NSCLC, and, specifically, the potential for interactions mediated via effects on gastrointestinal pH, cytochrome P450-dependent metabolism, uridine diphosphate-glucuronosyltransferase, and transporter proteins. We review evidence of such DDIs with the currently approved EGFR-TKIs (gefitinib, erlotinib, afatinib, osimertinib, and icotinib) and discuss several information sources that are available online to aid clinical decision-making. We conclude by summarizing the most clinically relevant DDIs with these EFGR-TKIs and provide recommendations for managing, minimizing, or avoiding DDIs with the different agents.
Keywords: drug metabolism, pharmacokinetics, CYP450, UDP-glucuronosyltransferase, P-glycoprotein