9 0 9 6 8
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 2.6 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.9 Clin Epidemiol
- 3.3 Cancer Manag Res
- 3.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.6 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.8 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.8 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 8.0 Int J Nanomed
- 2.3 Int J Women's Health
- 3.2 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 4.0 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.2 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.8 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.7 J Pain Res
- 3.3 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 4.3 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.9 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 3.5 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.5 J Inflamm Res
- 2.3 Int J Gen Med
- 4.1 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.2 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.3 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 3.3 J Multidiscip Healthc

作为 EGFR 酪氨酸激酶抑制剂耐药机制的获得性受体酪氨酸激酶融合的表征
Authors Xu H, Shen J, Xiang J, Li H, Li B, Zhang T, Zhang L, Mao X, Jian H, Shu Y
Received 6 December 2018
Accepted for publication 15 April 2019
Published 9 July 2019 Volume 2019:11 Pages 6343—6351
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S197337
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Ms Justinn Cochran
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Kenan Onel
Purpose: Responses to EGFR -targeted therapy are generally temporary, due to inevitable drug resistance. The prevalence and characteristics of receptortyrosine–kinase (RTK) fusion as acquired resistance to EGFR tyrosine–kinase inhibitors (TKIs) are rarely investigated.
Methods: We retrospectively reviewed genomic profiling data of 3873 EGFR (exons 18–21)-mutant lung cancer patients with more than once next-generation sequencing detection. A total of 16 patients who acquired RTK fusions during EGFR-TKI treatment with paired pre- and post-EGFR-TKI samples were identified. Their treatment history was collected.
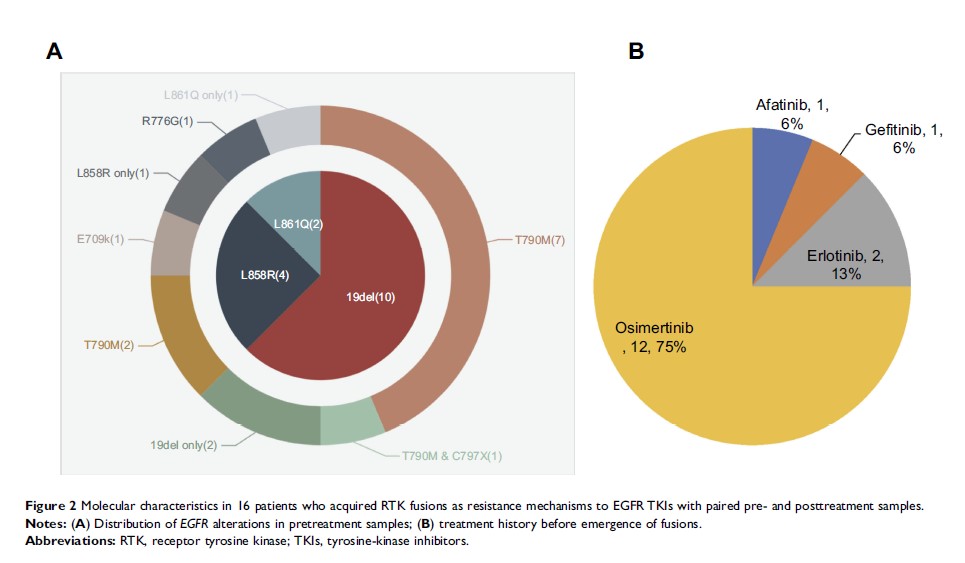
Results: Newly acquired RTK fusions during EGFR-TKI treatment included RET (n=6, 37.5%), ALK (n=5, 31.3%), NTRK1 (n=4, 25.0%), ROS1 (n=1, 6.3%), and FGFR3 (n=1, 6.3%). All RET and EML4 –ALK fusions were uncommon variants of KIF5B-RET and E2:A20 (V5), respectively. Interestingly, RET fusion occurred only after osimertinib treatment, and contributed to drug resistance in 50% (6 of 12) of patients treated with osimertinib, indicating that fusions had different prevalence when functioning as resistance mechanisms to EGFR TKIs. Moreover, we found that in all patients developing drug resistance to EGFR TKIs due to fusion emergence (n=16), those that had a treatment history of third-generation EGFR TKIs accounted for 75% (n=12).
Conclusion: We have extended the current knowledge of resistance mechanisms to EGFR TKIs in non-small-celllung cancer. Detection of RTK fusions should be included in genomic profiling panels to uncover potential resistance mechanisms of EGFR TKIs, which might inform therapeutic strategies, such as combination-therapy approaches, to circumvent tumorigenesis.
Keywords: receptor tyrosine kinase fusions, acquired resistance, EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors, lung cancer