9 0 9 6 8
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 2.6 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.9 Clin Epidemiol
- 3.3 Cancer Manag Res
- 3.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.6 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.8 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.8 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 8.0 Int J Nanomed
- 2.3 Int J Women's Health
- 3.2 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 4.0 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.2 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.8 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.7 J Pain Res
- 3.3 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 4.3 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.9 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 3.5 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.5 J Inflamm Res
- 2.3 Int J Gen Med
- 4.1 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.2 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.3 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 3.3 J Multidiscip Healthc

阴茎癌患者腹股沟淋巴结转移的预测因素:回顾性研究的荟萃分析
Authors Hu J, Cui Y, Liu P, Zhou X, Ren W, Chen J, Zu X
Received 23 February 2019
Accepted for publication 25 May 2019
Published 10 July 2019 Volume 2019:11 Pages 6425—6441
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S206579
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Melinda Thomas
Peer reviewer comments 4
Editor who approved publication: Dr Ahmet Emre Eskazan
Purpose: Inguinal lymph node metastasis (LNM) is one of the most significant prognostic factors for patients with penile cancer. This study aimed to identify potential predictors of inguinal LNM.
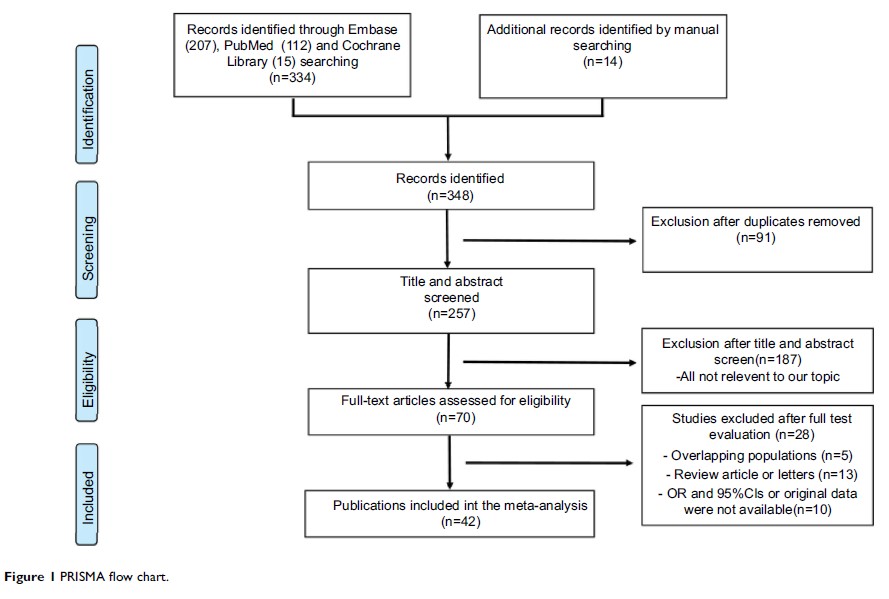
Patients and methods: A comprehensive search of the PubMed, Embase, and Cochrane Library databases for studies that reported predictors of inguinal LNM in penile cancer was performed. Finally, we selected 42 eligible studies with 4,802 patients. Accumulative analyses of odds ratios (ORs) and corresponding 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were performed. All analyses were performed by using Review Manager software version 5.3.
Results: Among the 4,802 patients, 1,706 (36%) were diagnosed with inguinal LNM. Predictors of LNM included two categories: tumor-associated biomarkers and invasive clinicopathologic characteristics. Biomarker-specific predictors: the program death ligand 1 (PD-L1) overexpression (OR=2.55, p =0.002), higher neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) (OR=4.22, p =0.010), higher C-reactive protein (CRP) (OR=4.78, p <0.001), squamous cell carcinoma antigen (SCC-Ag) overexpression (OR=8.52, p <0.001), P53 protein overexpression (OR=3.57, p <0.001). Clinicopathological predictors: positive clinical lymph node (cN+) (OR=5.86, p <0.001), high-risk histopathological subtype (OR=14.63, p <0.001) and intermediate-risk subtype (OR=3.37, p <0.001), vertical growth pattern (OR=1.97, p =0.020), higher stage (AJCC: OR=3.66, p <0.001; UICC: OR=2.43, p <0.001), higher tumor grade (OR=3.37, p <0.001), tumor size (>3 cm) (OR=2.00, p =0.002), LVI (OR=3.37, p <0.001), invasion depth (>5 mm) (OR=2.58, p =0.002), nerve invasion (OR=2.84, p <0.001), corpora cavernosum invasion (OR=2.22, p <0.001), corpus spongiosum invasion (OR=1.73, p =0.002) and urethra invasion (OR=1.81, p =0.030).
Conclusion: Current meta-analysis conclusively identified valuable predictors of inguinal LNM for patients with penile cancer. However, high-quality studies are warranted to further validate our conclusions. The intrinsic link between these predictors needs to be further investigated to create an accurate mathematical prediction model for LNM.
Keywords: inguinal lymph node metastasis, penile cancer, predictor, meta-analysis