9 0 9 6 8
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 2.6 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.9 Clin Epidemiol
- 3.3 Cancer Manag Res
- 3.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.6 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.8 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.8 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 8.0 Int J Nanomed
- 2.3 Int J Women's Health
- 3.2 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 4.0 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.2 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.8 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.7 J Pain Res
- 3.3 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 4.3 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.9 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 3.5 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.5 J Inflamm Res
- 2.3 Int J Gen Med
- 4.1 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.2 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.3 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 3.3 J Multidiscip Healthc

人参皂甙 Rg1 可改善链脲佐菌素诱导的糖尿病大鼠心脏氧化应激和炎症反应
Authors Qin Q, Lin N, Huang H, Zhang X, Cao X, Wang Y, Li P
Received 16 March 2019
Accepted for publication 22 May 2019
Published 10 July 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 1091—1103
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DMSO.S208989
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Melinda Thomas
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Antonio Brunetti
Background and purpose: Ginsenoside Rg1 (GS Rg1), as an important active substance of Panax ginseng, has been proven to have elaborate cardioprotective effects. The purpose of this study was to detect that GS Rg1 attenuates cardiac oxidative stress and inflammation in streptozotocin (STZ)-induced diabetic rats (DM).
Methods: Cardiac function was assessed by heart rate and blood pressure. Markers relevant to myocardial oxidative stress and antioxidant capacity, and inflammatory reaction factors were detected. The mRNA and protein expression were detected by RT-qPCR and Western blot, respectively.
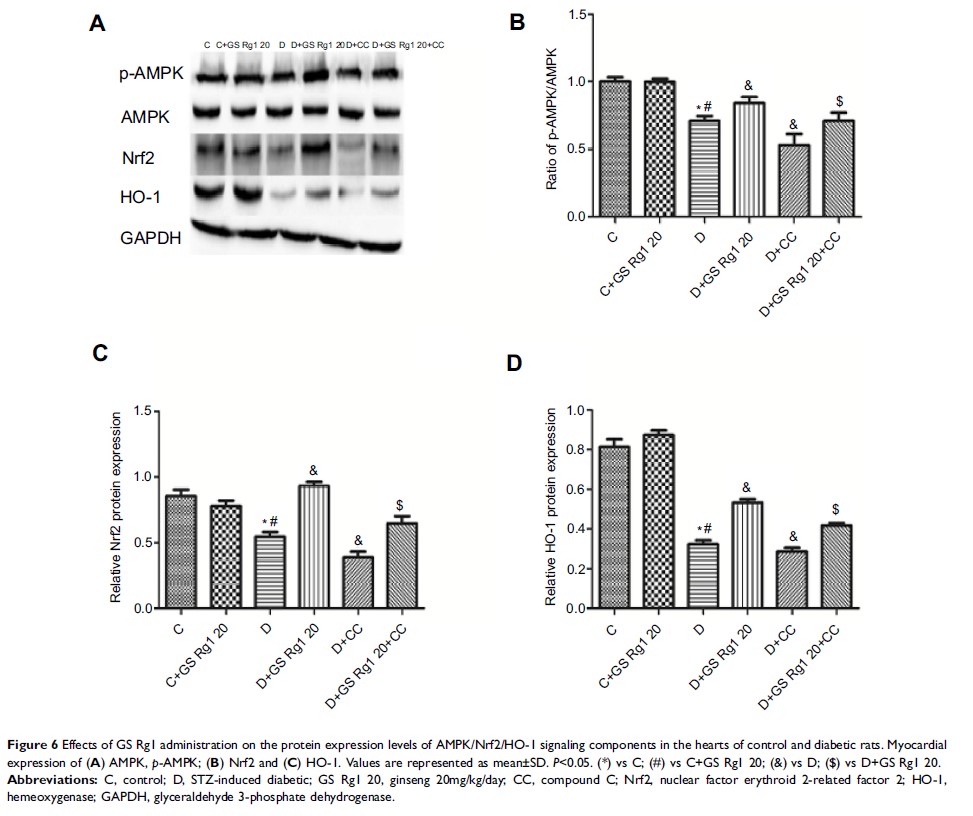
Results: GS Rg1 treatment significantly reduced the symptoms of cardiac hypertrophy and hypertension, and also decreased oxidative stress, inflammation response, NF-κB expression and NLRP3 inflammasome expression. GS Rg1 enhanced mitochondrial biogenesis by increasing PGC-1α, complex III and complex Ⅳ expression. GS Rg1 treatment significantly increased the expression of AMPK, Nrf2 and HO-1 in cardiac tissues.
Conclusion: GS Rg1 exhibited protective effect against STZ-induced cardiac dysfunction, which is potentially associated with AMPK/Nrf2/HO-1 signal pathway.
Keywords: Ginsenoside Rg1, oxidative stress, inflammation, AMPK, Nrf, HO-1