9 0 8 1 0
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 2.6 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.9 Clin Epidemiol
- 3.3 Cancer Manag Res
- 3.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.6 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.8 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.8 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 8.0 Int J Nanomed
- 2.3 Int J Women's Health
- 3.2 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 4.0 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.2 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.8 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.7 J Pain Res
- 3.3 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 4.3 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.9 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 3.5 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.5 J Inflamm Res
- 2.3 Int J Gen Med
- 4.1 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.2 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.3 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 3.3 J Multidiscip Healthc

顺铂与基于四间羟基苯基二氢卟酚的光动力疗法对恶性 Hep-2 细胞的协同作用
Authors Xue K, Wang YN, Zhao X, Zhang HX, Yu D, Jin CS
Received 16 December 2018
Accepted for publication 12 May 2019
Published 10 July 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 5525—5536
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S198422
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Ms Aruna Narula
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Takuya Aoki
Purpose: Tumor drug resistance limits the response to chemotherapy. Interestingly, sequential combination therapy enhances the anticancer efficacy of drugs like cisplatin (CDDP) via synergistic effects. We assayed the synergistic effects of combined photodynamic therapy programmed death receptor-ligand 1 (PDT) and chemotherapy in malignant Hep-2 cells.
Methods: In the cultured Hep-2 cells, meta-tetra(hydroxyphenyl)chlorin (m-THPC) and CDDP were administered separately or in combination. The cellular viability and apoptosis were assessed, accompanied by measurement of the expression of Bax, Bcl-2, ATG-7, and LC3 (LC3-I and LC3-II). Additionally, nuclear chromatin changes, drug retention, and PD-L1 expression were further investigated following different treatments.
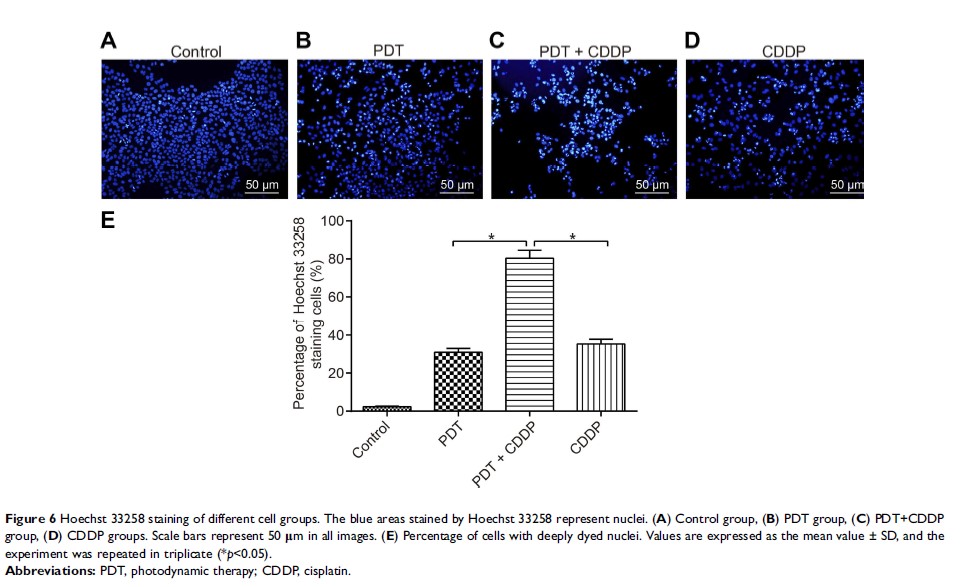
Results: The sequential treatment significantly diminished cell viability and induced cell apoptosis, in consistency with the usage of single therapeutic strategies, as reflected by an increase in Bax expression and decrease of Bcl-2 expression. Moreover, ATG-7 and LC3-II/LC3-I ratio were reduced after administration of the sequential treatment. Synergetic effect of nuclear chromatin configuration, negative effects of cellular drug retention, and a decrease in PD-L1 expression were observed following the sequential treatment.
Conclusion: The application of sequential treatment of PDT in combination with chemotherapy offers a promising therapeutic option for cancer treatment, by regulating the PD-L1 expression, autophagy, and non-mitochondrial pathways.
Keywords: photodynamic therapy, sequential treatment, chemotherapy, PD-L1, Hep-2 cell