9 0 8 1 0
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 2.6 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.9 Clin Epidemiol
- 3.3 Cancer Manag Res
- 3.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.6 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.8 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.8 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 8.0 Int J Nanomed
- 2.3 Int J Women's Health
- 3.2 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 4.0 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.2 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.8 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.7 J Pain Res
- 3.3 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 4.3 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.9 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 3.5 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.5 J Inflamm Res
- 2.3 Int J Gen Med
- 4.1 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.2 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.3 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 3.3 J Multidiscip Healthc

中国汉族双相情感障碍患者锂盐治疗的血药浓度相关因素
Authors Xu YY, Xia QH, Liang J, Cao Y, Shan F, Liu Y, Yan CY, Xia QR
Received 17 February 2019
Accepted for publication 17 June 2019
Published 10 July 2019 Volume 2019:15 Pages 1929—1937
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/NDT.S205780
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Yu-Ping Ning
Background: The goal of this study was to identify the physiological factors related to the blood concentration of lithium in Chinese Han patients with bipolar disorder (BD).
Materials and methods: A total of 186 Chinese Han patients with BD were assessed. Patients were recruited from the Anhui Mental Health Center. The concentrations of serum lithium were measured by a Dimension RxL Max biochemistry analyzer. Physiological factors, including body weight, body mass index (BMI), and routine laboratory parameters, were collected. Relationships between the serum lithium concentration and relevant clinical data were analyzed by Pearson correlation tests, and the independent relationships were determined by multivariate linear regression analysis.
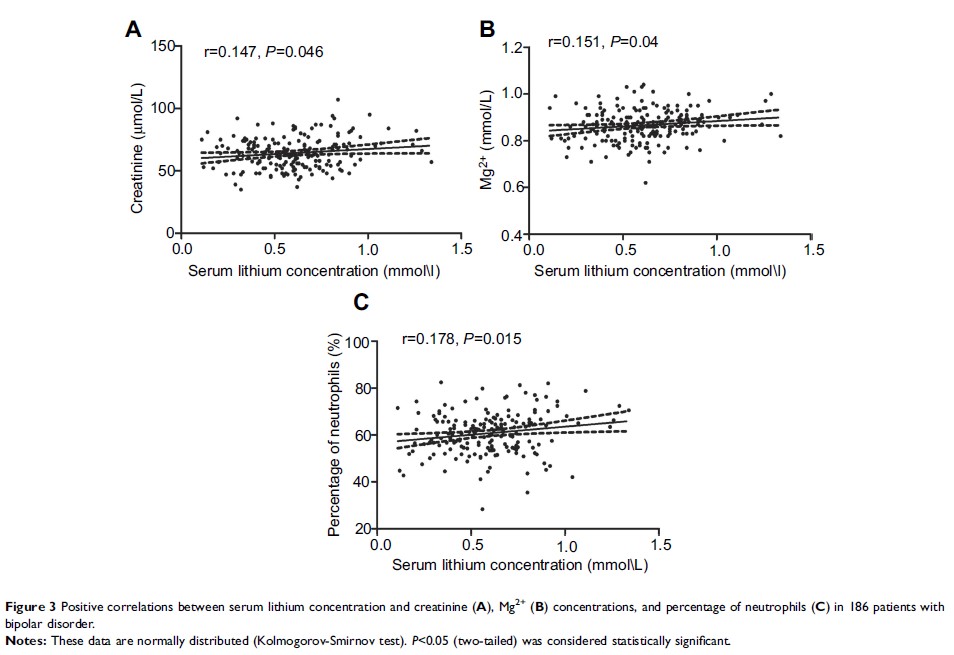
Results: Pearson correlation analysis showed that serum lithium concentrations were positively correlated with creatinine concentrations (r=0.147, P =0.046), Mg2+ concentrations (r=0.151, P =0.04), and the percentage of neutrophils (r=0.178, P =0.015) and negatively correlated with high-density lipoprotein (HDL) concentrations (r=−0.142, P =0.05), apolipoprotein A1 concentrations (r=−0.169, P =0.02), and Na+ concentrations (r=−0.148, P =0.046) in 186 patients with BD. Furthermore, multivariate linear regression analysis showed that serum lithium concentrations were negatively associated with Na+ concentrations and positively associated with the percentage of neutrophils.
Conclusion: These results suggest that physiological factors, including creatinine, HDL, apolipoprotein A1, Na+, and Mg2+ concentrations and percentage of neutrophils, might be related to serum lithium concentrations and provide a basis for parameter selection of lithium population pharmacokinetics in Chinese Han patients with BD.
Keywords: bipolar disorder, apolipoprotein A1, creatinine, high-density lipoprotein, neutrophil, lithium