9 0 8 1 0
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 2.6 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.9 Clin Epidemiol
- 3.3 Cancer Manag Res
- 3.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.6 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.8 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.8 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 8.0 Int J Nanomed
- 2.3 Int J Women's Health
- 3.2 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 4.0 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.2 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.8 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.7 J Pain Res
- 3.3 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 4.3 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.9 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 3.5 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.5 J Inflamm Res
- 2.3 Int J Gen Med
- 4.1 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.2 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.3 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 3.3 J Multidiscip Healthc

海马的 UPLC-Q-TOF-MS 谱分析揭示了 Dl-3-正丁基苯酞对脂多糖诱导的抑郁症大鼠模型所产生影响的代谢物生物标志物
Authors Geng C, Guo Y, Qiao Y, Zhang J, Chen D, Han W, Yang M, Jiang P
Received 1 February 2019
Accepted for publication 10 June 2019
Published 10 July 2019 Volume 2019:15 Pages 1939—1950
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/NDT.S203870
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Prof. Dr. Roumen Kirov
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Yu-Ping Ning
Purpose: An increasing body of evidence reveals that inflammation is involved in the pathological mechanisms of depression. Our previous basic research confirmed that Dl-3-n-butylphthalide (NBP) possess anti-inflammatory properties. However, studies investigating metabolite biomarkers for the involvement of NBP in hippocampus tissue in the lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced rat model of depression are currently limited. Thus, the aim of this study was to identify metabolite biomarkers in the hippocampus for the impact of NBP in this model of depression.
Material and methods: Male Sprague–Dawley rats were randomly allocated to one of the following three groups (n=6): Control, LPS-induced rat model of depression (LPS), and NBP involvement in the LPS-induced rat model of depression (LPS+NBP). Ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography-mass spectroscopy was used to determine the hippocampal metabolites. Multivariate statistical analysis was performed to identify differentially expressed hippocampal metabolites in the three groups.
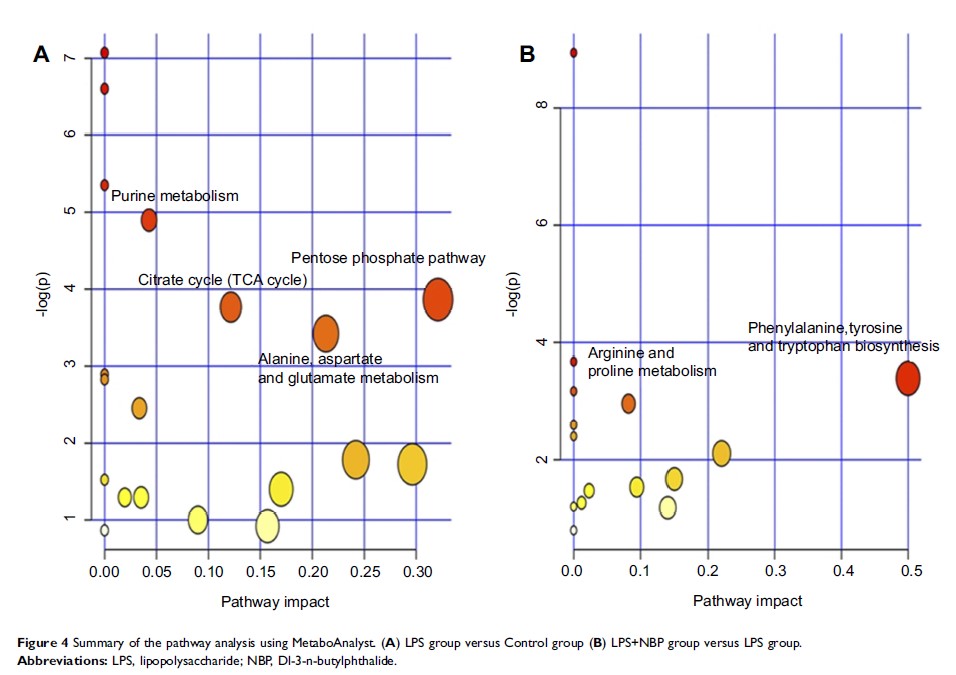
Results: Most of the identified differentially expressed metabolites were related to amino acid, lipid, energy, and oxidative stress metabolism. Additionally, metabolites were eventually connected to different pathways and metabolic networks, which may partly account for the pathophysiological process of depression.
Conclusion: The present findings provide insight into the anti-inflammatory effects of NBP, and further elucidate the pathophysiological mechanisms underlying inflammation-induced depression.
Keywords: inflammation, Dl-3-n-butylphthalide, lipopolysaccharide, metabolite biomarkers, ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography-mass spectroscopy