9 0 8 1 0
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 2.6 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.9 Clin Epidemiol
- 3.3 Cancer Manag Res
- 3.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.6 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.8 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.8 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 8.0 Int J Nanomed
- 2.3 Int J Women's Health
- 3.2 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 4.0 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.2 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.8 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.7 J Pain Res
- 3.3 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 4.3 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.9 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 3.5 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.5 J Inflamm Res
- 2.3 Int J Gen Med
- 4.1 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.2 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.3 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 3.3 J Multidiscip Healthc

cGAS/STING 通路:与衰老相关的 DNA 损伤传感器和早期年龄相关性黄斑变性的炎症触发因素
Authors Wu Y, Wei Q, Yu J
Received 7 January 2019
Accepted for publication 10 June 2019
Published 11 July 2019 Volume 2019:14 Pages 1277—1283
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CIA.S200637
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Melinda Thomas
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Zhi-Ying Wu
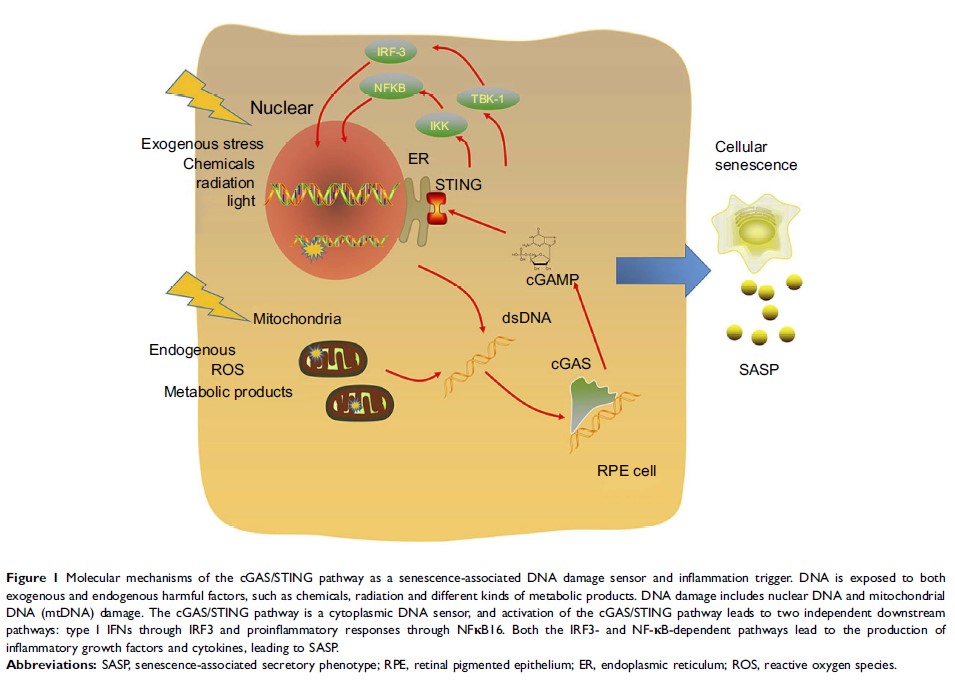
Abstract: Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) is the leading cause of irreversible blindness among the elderly. Considering the relatively limited effect of therapy on early AMD, it is important to focus on the pathogenesis of AMD, especially early AMD. Ageing is one of the strongest risk factors for AMD, and analysis of the impact of ageing on AMD development is valuable. Among all the ageing hallmarks, increased DNA damage accumulation is regarded as the beginning of cellular senescence and is related to abnormal expression of inflammatory cytokines, which is called the senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP). The exact pathway for DNA damage that triggers senescence-associated hallmarks is poorly understood. Recently, mounting evidence has shown that the cGAS/STING pathway is an important DNA sensor related to proinflammatory factor secretion and is associated with another hallmark of ageing, SASP. Thus, we hypothesized that the cGAS/STING pathway is a vital signalling pathway for early AMD development and that inhibition of STING might be a potential therapeutic strategy for AMD cases.
Keywords: age-related macular degeneration, cGAS/STING pathway, DNA damage, inflammation