9 0 8 1 0
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 2.6 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.9 Clin Epidemiol
- 3.3 Cancer Manag Res
- 3.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.6 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.8 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.8 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 8.0 Int J Nanomed
- 2.3 Int J Women's Health
- 3.2 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 4.0 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.2 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.8 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.7 J Pain Res
- 3.3 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 4.3 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.9 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 3.5 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.5 J Inflamm Res
- 2.3 Int J Gen Med
- 4.1 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.2 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.3 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 3.3 J Multidiscip Healthc

Linc00467 通过海绵状 miR-20b-5p 促进肺腺癌增殖并激活 CCND1 表达
Authors Ding H, Luo Y, Hu K, Liu P, Xiong M
Received 6 March 2019
Accepted for publication 16 July 2019
Published 21 August 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 6733—6743
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S207748
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Ms Aruna Narula
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Leo Jen-Liang Su
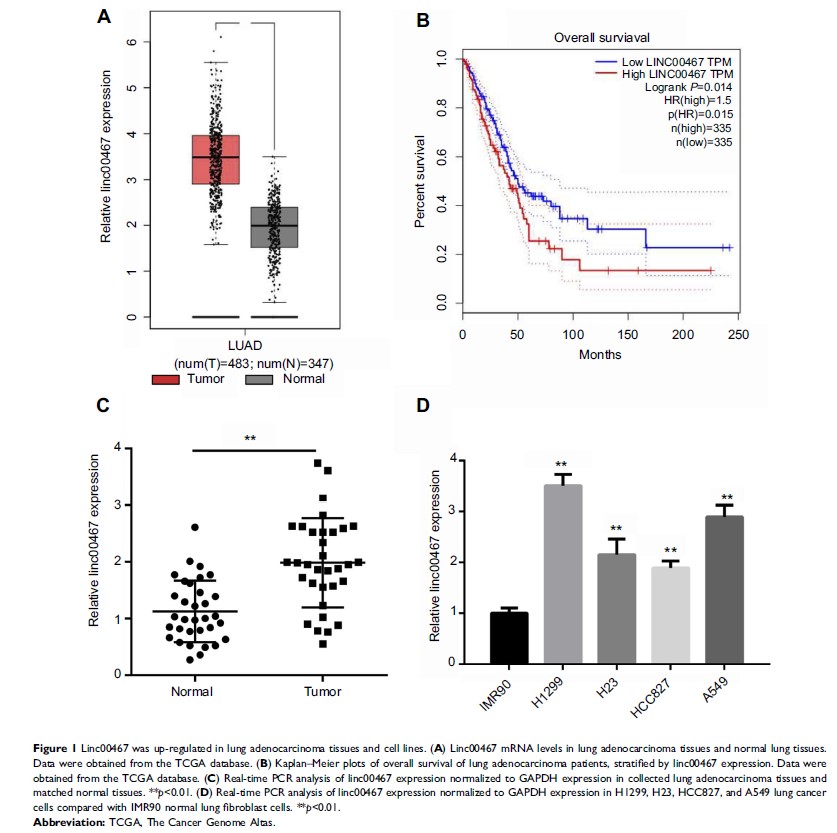
Background: Recently, numerous studies have demonstrated the emerging role of long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) in human cancers. Linc00467 is a newly defined lncRNA and was reported to promote cell survival in neuroblastoma. However, the function of linc00467 in lung cancer is still unclear.
Material and methods: We analyzed linc00467 expression and survival data derived from The Cancer Genome Altas lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) dataset as well as in collected LUAD tissues. Then, we silenced linc00467 expression in two lung cancer cell lines using small interfering RNAs and explored the effect of linc00467 knockdown on cell growth in vitro and in vivo. Moreover, we revealed a novel target gene of linc00467 and elucidated the underlying competitive endogenous RNA regulatory mechanism in lung cancer cells.
Results: Our data suggested that linc00467 expression was elevated in LUAD tissues and correlated with overall survival of LUAD patients. Linc00467 knockdown resulted in reduced proliferation rate in lung cancer cells. Furthermore, we elucidated that linc00467 promoted CCND1 expression in lung cancer cells via functioning as a molecular sponge for miR-20b-5p.
Conclusion: Linc00467/miR-20b-5p/CCND1 signaling pathway may provide new insights into lung cancer treatment.
Keywords: linc00467, lung adenocarcinoma, cell growth, miR-20b-5p, CCND1