9 1 2 3 6
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 2.6 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.9 Clin Epidemiol
- 3.3 Cancer Manag Res
- 3.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.6 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.8 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.8 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 8.0 Int J Nanomed
- 2.3 Int J Women's Health
- 3.2 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 4.0 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.2 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.8 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.7 J Pain Res
- 3.3 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 4.3 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.9 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 3.5 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.5 J Inflamm Res
- 2.3 Int J Gen Med
- 4.1 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.2 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.3 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 3.3 J Multidiscip Healthc

miR-410-3p 的表达降低与人脑胶质瘤的不良预后和肿瘤发生有关
Authors Wang C, Huang S, Rao S, Hu J, Zhang Y, Luo J, Wang H
Received 20 January 2019
Accepted for publication 30 April 2019
Published 18 December 2019 Volume 2019:11 Pages 10581—10592
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S202247
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Rituraj Purohit
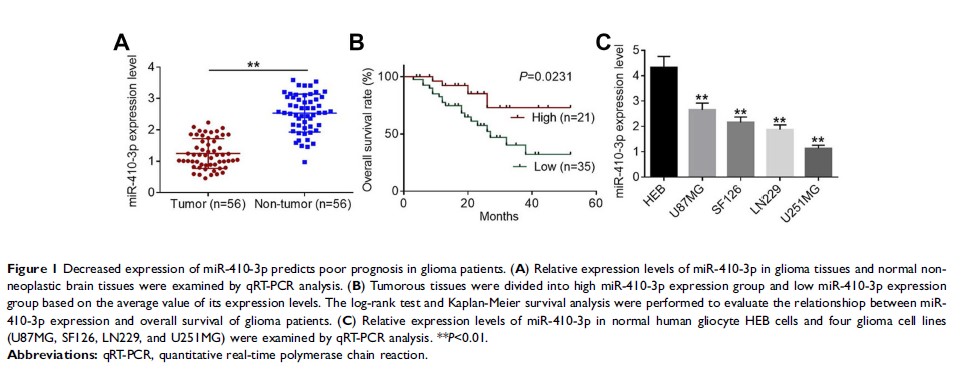
Background: Gliomas are the most common type of primary tumors in the central nervous system. This study aimed to investigate the biological role of miR-410-3p in glioma and elucidate the potential molecular mechanisms involved.
Methods: The expression levels of miR-410-3p in clinical tissue samples and glioma cell lines were determined using qRT-PCR analysis. The clinical significance of miR-410-3p in glioma was evaluated using Kaplan-Meier survival analysis and Fisher’s exact test. The effects of miR-410-3p on glioma cell proliferation, apoptosis, migration and invasion were investigated using MTT assays, flow cytometry, transwell migration and invasion assays. Besides, corresponding mechanistic studies were carried out.
Results: miR-410-3p was significantly down-regulated in glioma tissues. Besides, Kaplan-Meier analysis demonstrated that patients with low miR-410-3p expression had a shorter overall survival. Decreased miR-410-3p expression was associated with larger tumor size, lower Karnofsky performance score (KPS), and higher World Health Organization (WHO) grade. Over-expression of miR-410-3p suppressed cell proliferation, migration, and invasion, and accelerated apoptosis; whereas depletion of miR-410-3p facilitated cell proliferation, migration, and invasion, and inhibited apoptosis. Mechanistic investigations demonstrated that Ras-related protein 1A (RAP1A) was a direct target of miR-410-3p, and that rescue of RAP1A expression reversed miR-410-3p over-expression-induced inhibitory effects on cell proliferation, migration, and invasion. Notably, miR-410-3p over-expression repressed tumor growth in mouse xenograft models.
Conclusion: Our findings indicate that miR-410-3p functions as a tumor suppressor in glioma by directly targeting RAP1A. Thus, this study may provide some new insights into gliomagenesis and progression.
Keywords: miR-410-3p, RAP1A, poor prognosis, tumorigenesis, glioma