9 1 2 3 6
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 2.6 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.9 Clin Epidemiol
- 3.3 Cancer Manag Res
- 3.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.6 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.8 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.8 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 8.0 Int J Nanomed
- 2.3 Int J Women's Health
- 3.2 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 4.0 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.2 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.8 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.7 J Pain Res
- 3.3 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 4.3 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.9 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 3.5 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.5 J Inflamm Res
- 2.3 Int J Gen Med
- 4.1 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.2 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.3 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 3.3 J Multidiscip Healthc

CSF2 的去甲基化和过表达与结直肠癌的免疫应答、化疗耐药性和不良预后有关
Authors Xu Z, Zhang Y, Xu M, Zheng X, Lin M, Pan J, Ye C, Deng Y, Jiang C, Lin Y, Lu X, Chi P
Received 23 May 2019
Accepted for publication 13 September 2019
Published 19 December 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 11255—11269
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S216829
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 4
Editor who approved publication: Dr William Cho
Purpose: This study aimed to evaluate the role of colony-stimulating factor 2 (CSF2) in chemotherapy resistance, prognosis, and immune response and to identify its possible mechanisms underlying drug resistance.
Methods: Drug-resistant cell lines were obtained by successively increasing drug concentration. RNA-Seq was performed to screen hub genes. CSF2 expression was analyzed via immunohistochemistry. Moreover, The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA), Tumor Immune Estimation Resource (TIMER) dataset, and R2 platform were used to explore the correlations among CSF2 expression, prognosis, and immune response.
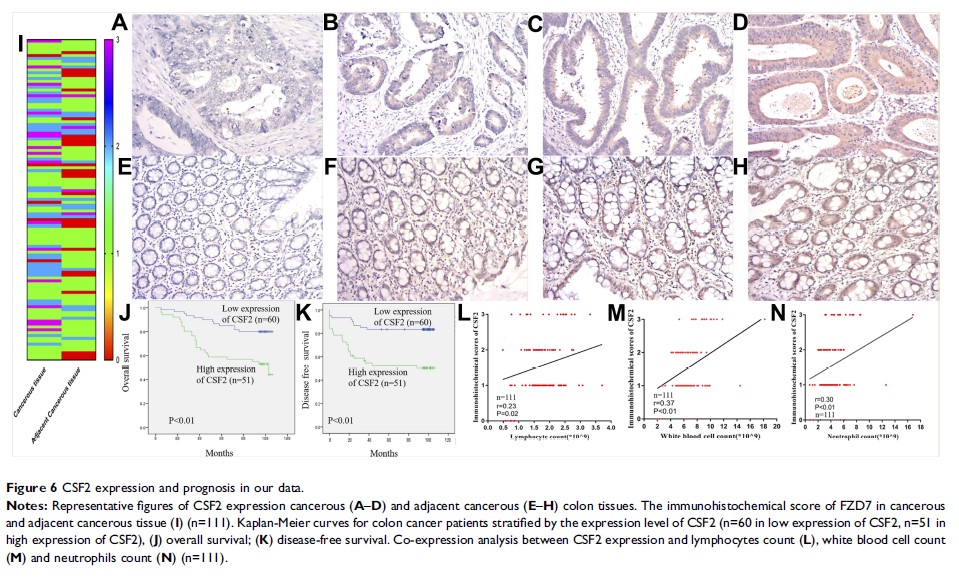
Results: RNA-Seq indicated that microRNAs in cancer, P53 signaling pathway, and cell cycle were associated with FOLFOX chemotherapy resistance. Protein-protein interaction (PPI), molecular complex detection (MOCDE), and qRT-PCR analysis verified CSF2 as the hub gene in chemotherapy resistance. Moreover, CSF2 expression was lower in the normal tissue than in the cancerous tissue (P<0.05). Higher expression of CSF2 was associated with poor OS and DFS in colon cancer patients (P<0.05). We further found similar results in the Oncomine database and R2 platform (P<0.05). A higher expression of CSF2 in the CRC tissue may be caused by demethylation, which was verified using the TCGA datasets. Moreover, GSEA demonstrated that CSF2 was associated with immune response, which was consistent with results reported using TIMER datasets.
Conclusion: CSF2 is a novel biomarker and a prognostic factor for the survival of CRC patients affecting the immune response, and an overexpression of CSF2 in CRC patients may be caused by DNA demethylation.
Keywords: colorectal cancer, FOLFOX, prognosis, CSF2, immune response