9 0 8 1 0
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 2.6 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.9 Clin Epidemiol
- 3.3 Cancer Manag Res
- 3.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.6 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.8 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.8 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 8.0 Int J Nanomed
- 2.3 Int J Women's Health
- 3.2 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 4.0 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.2 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.8 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.7 J Pain Res
- 3.3 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 4.3 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.9 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 3.5 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.5 J Inflamm Res
- 2.3 Int J Gen Med
- 4.1 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.2 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.3 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 3.3 J Multidiscip Healthc

接受血管内皮生长因子受体酪氨酸激酶抑制剂治疗的癌症患者的严重感染的风险: 一项综合分析
Authors Ma Q, Gu LY, Ren YY, Zeng LL, Gong T, Zhong DS
Received 24 April 2015
Accepted for publication 25 May 2015
Published 28 August 2015 Volume 2015:8 Pages 2361—2374
DOI http://dx.doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S87298
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 5
Editor who approved publication: Professor Daniele Santini
Background: Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors (VEGFR-TKIs) have been widely used in a variety of solid malignancies. Concerns have arisen regarding the risk of severe infections (≥grade 3) with use of these drugs, but the contribution of VEGFR-TKIs to infections is still unknown.
Methods: The databases of PubMed and abstracts presented at oncology conferences’ proceedings were searched for relevant studies from January 2000 to December 2014. Summary incidences, Peto odds ratio (Peto OR), and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were calculated by using either random-effects or fixed-effects models according to
the heterogeneity of included studies.
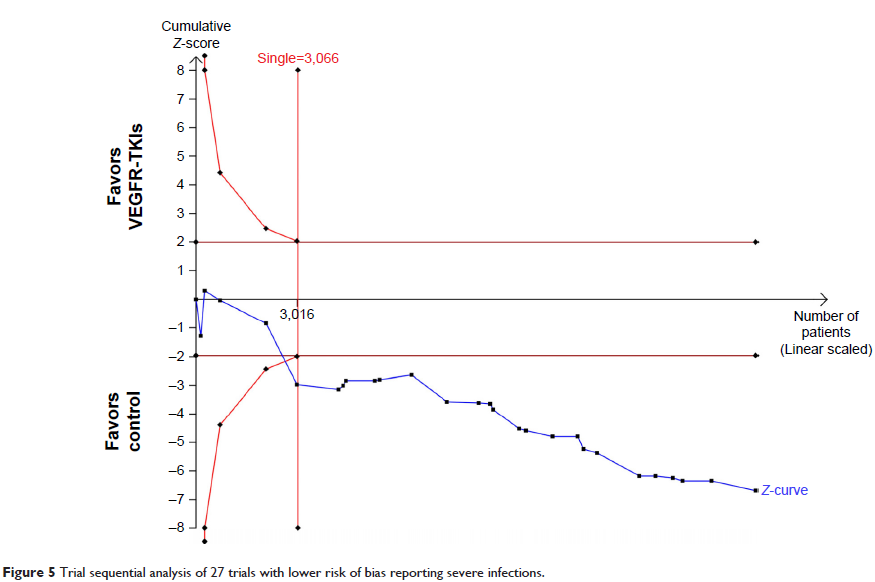
Results: A total of 16,488 patients from 27 randomized controlled trials were included. The risk of developing severe (Peto OR 1.69, 95% CI: 1.45–1.96, P <0.001) and fatal infections (Peto OR 1.78, 95% CI: 1.13–2.81, P =0.013) was significantly increased in patients treated with VEGFR-TKIs when compared to controls. Exploratory subgroup analysis showed no effect of tumor types, phase of trials, or agent used on the Peto OR of severe infections. When stratified according to specific infectious events, the risks of high-grade febrile neutropenia, pneumonia, fever, and sepsis were increased compared with controls, with Peto ORs of 1.57 (95% CI: 1.30–1.88, P <0.001), 1.79 (95% CI: 1.29–2.49, P <0.001), 5.35 (95% CI: 1.47–19.51, P =0.011), and 3.68 (95% CI: 1.51–8.99, P =0.004), respectively. Additionally, VEGFR-TKIs significantly increased the risk of fatal sepsis (OR 3.66, 95% CI: 1.47–9.13, P =0.005) but not fatal pneumonia (OR 1.34, 95% CI: 0.80–2.25, P =0.26).
Conclusion: The use of VEGFR-TKIs significantly increases the risk of developing severe and fatal infectious events in cancer patients. A close monitoring for any signs of infections is recommended for patients treated with VEGFR-TKIs.
Keywords: VEGFR-TKIs, infections, cancer, randomized controlled trials, meta-analysis