111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

靶向外分泌体作为阿尔茨海默氏病的新生物标记和治疗方法
Authors Yin Q, Ji X, Lv R, Pei JJ, Du Y, Shen C, Hou X
Received 28 November 2019
Accepted for publication 3 February 2020
Published 13 February 2020 Volume 2020:15 Pages 195—205
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CIA.S240400
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Zhi-Ying Wu
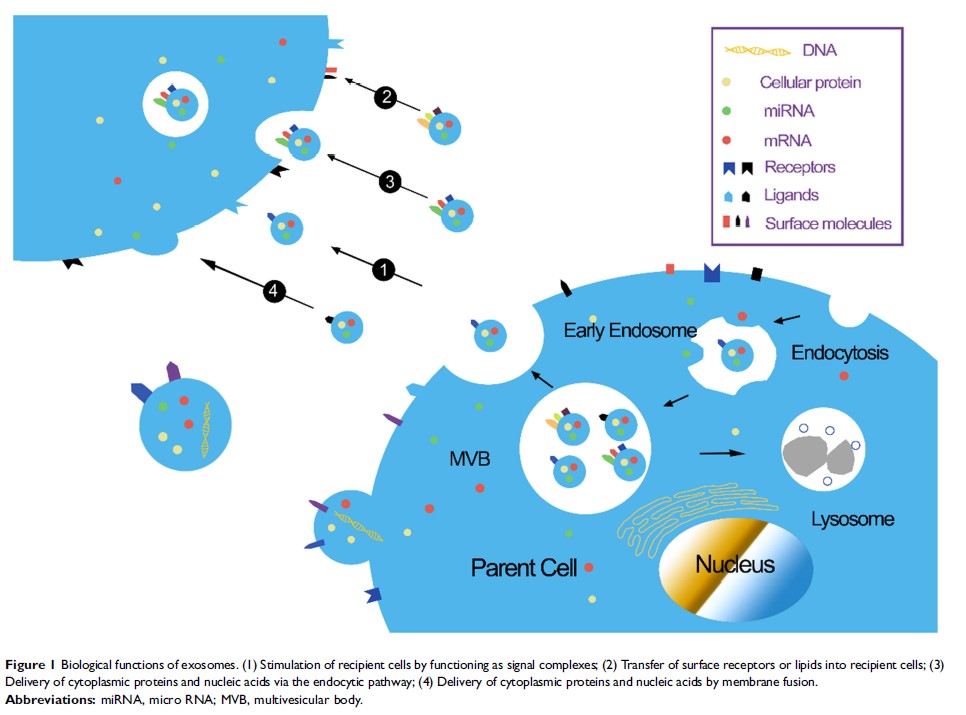
Abstract: Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative disease that mainly occurs in old age and involves progressive cognitive impairment. AD has become a major global issue for public health, with approximately 24 million people currently affected by the disease. Estimates indicted that this number will quadruple by 2050. Because of the high incidence of AD, there is an urgent need to develop new strategies to diagnose and treat AD. Many recent studies have indicated the multiple, yet somewhat controversial, roles of exosomes in AD. Although the underlying mechanisms by which exosomes play a role in AD are still unknown, current evidence suggests that exosomes can carry and spread toxic amyloid-beta, and hyperphosphorylated tau, between cells, and then induce apoptosis, thus contributing to the loss of neurons. In addition, exosomes appear to possess the ability to reduce brain amyloid-beta, and tau hyperphosphorylation, and transfer neuroprotective substances between neural cells. The accumulating data brings hope that the application of exosomes may be helpful for early diagnostics and the identification of new therapeutic targets for AD. Here, we summarized the various roles of exosomes, and how they might relate to the pathogenesis of AD. We also highlight the potential application of exosomes as a therapeutic option in AD therapy.
Keywords: exosomes, alzheimer’s disease, biomarker, mesenchymal stem cells, therapeutic strategy