111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

载有甘草素的亚微米乳剂可通过抗氧化、抗炎和抗凋亡活性来防止阿霉素诱导的心脏毒性
Authors Shi C, Wu H, Xu K, Cai T, Qin K, Wu L, Cai B
Received 23 October 2019
Accepted for publication 1 February 2020
Published 17 February 2020 Volume 2020:15 Pages 1101—1115
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S235832
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Thomas Webster
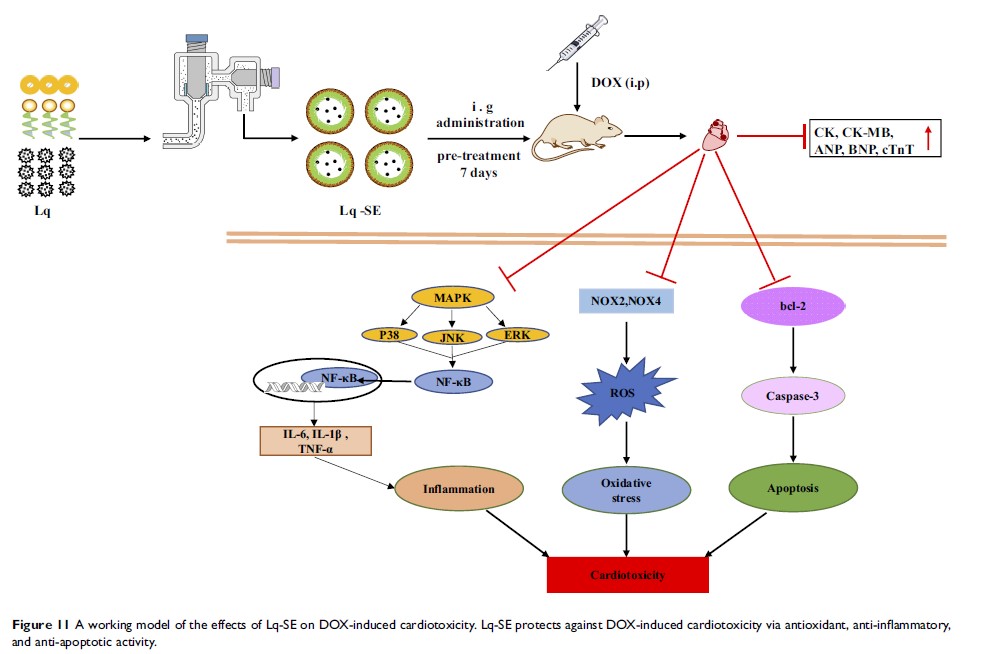
Background: The clinical use of doxorubicin (DOX) is severely limited due to its cardiotoxicity. Thus, there is a need for prophylactic and treatment strategies against DOX-induced cardiotoxicity.
Purpose: The purpose of this study was to develop a liquiritigenin-loaded submicron emulsion (Lq-SE) with enhanced oral bioavailability and to explore its efficacy against DOX-induced cardiotoxicity.
Methods: Lq-SE was prepared using high-pressure homogenization and characterized using several analytical techniques. The formulation was optimized by central composite design response surface methodology (CCD-RSM). In vivo pharmacokinetic studies, biochemical analyses, reactive oxygen species (ROS) assays, histopathologic assays, and Western blot analyses were performed.
Results: Each Lq-SE droplet had a mean particle size of 221.7 ± 5.80 nm, a polydispersity index (PDI) of 0.106 ± 0.068 and a zeta potential of − 28.23 ± 0.42 mV. The area under the curve (AUC) of Lq-SE was 595% higher than that of liquiritigenin (Lq). Lq-SE decreased the release of serum cardiac enzymes and ameliorated histopathological changes in the hearts of DOX-challenged mice. Lq-SE significantly reduced oxidative stress by adjusting the levels of ROS, increasing the activity of antioxidative enzymes and inhibiting the protein expression of NOX4 and NOX2. Furthermore, Lq-SE significantly improved the inflammatory response through the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK)/nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) signalling pathway and induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis.
Conclusion: Lq-SE could be used as an effective cardioprotective agent against DOX in chemotherapy to enable better treatment outcomes.
Keywords: liquiritigenin, submicron emulsion, bioavailability, cardiotoxicity, protective efficacy