111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

肝细胞癌的靶向治疗:使用乳糖基化、pH 响应的纳米颗粒共同递送索拉非尼和姜黄素
Authors Bian Y, Guo D
Received 17 November 2019
Accepted for publication 11 January 2020
Published 18 February 2020 Volume 2020:14 Pages 647—659
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S238955
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Tuo Deng
Purpose: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a leading cancer worldwide. In the present investigation, sorafenib (SFN) and curcumin (CCM) were co-delivered using pH-sensitive lactosylated nanoparticles (LAC-NPs) for targeted HCC treatment.
Methods: pH-responsive lactosylated materials were synthesized. SFN and CCM co-delivered, pH-responsive lactosylated nanoparticles (LAC-SFN/CCM-NPs) were self-assembled by using the nanoprecipitation technique. The nanoparticles were characterized in terms of particle size, charge and drug release profile. The anti-cancer effects of the nanoparticles were evaluated in human hepatic carcinoma cells (HepG2) cells and HCC tumor xenograft models.
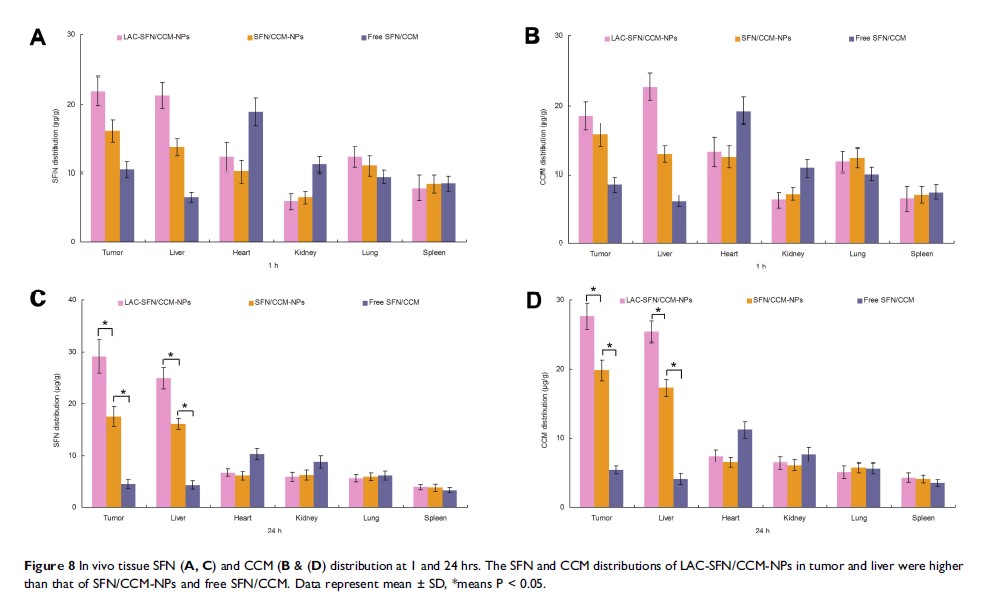
Results: LAC-SFN/CCM-NPs are spherical particles with light coats on the surface. The size and zeta potential of LAC-SFN/CCM-NPs were 115.5 ± 3.6 nm and − 34.6 ± 2.4, respectively. The drug release of LAC-SFN/CCM-NPs in pH 5.5 was more efficient than in pH 7.4. LAC-SFN/CCM-NPs group exhibited the smallest tumor volume (239 ± 14 mm3), and the inhibition rate of LAC-SFN/CCM-NPs was 77.4%.
Conclusion: In summary, LAC-SFN/CCM-NPs was proved to be a promising system for targeted HCC therapy.
Keywords: hepatocellular carcinoma, nanoparticles, pH-responsive, sorafenib, curcumin