111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

被激活的肝星状细胞(HSC)通过产生补体 C3 在肝细胞癌中发挥免疫抑制作用
Authors Xu Y, Huang Y, Xu W, Zheng X, Yi X, Huang L, Wang Y, Wu K
Received 16 October 2019
Accepted for publication 1 February 2020
Published 18 February 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 1497—1505
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S234920
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Gaetano Romano
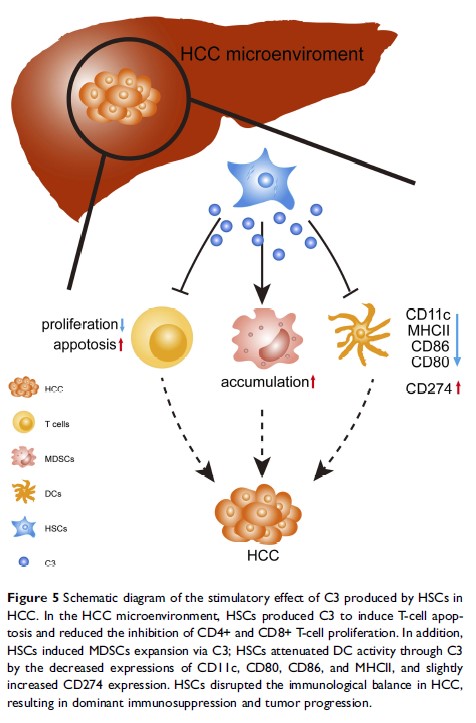
bjective: Hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) are the important players in liver cirrhosis and liver cancer. They also act as critical mediators of immunosuppression in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). In this study, we hypothesized that HSCs promote HCC progression via C3.
Methods: C3 in HSCs was knocked down using a shRNA retroviral plasmid. The conditioned medium from HSCs or shC3 HSCs (knockdown of C3 by shRNA in HSCs) was collected to detect their effects on bone marrow (BM) and T cells (including expansion and apoptosis) in vitro, and in an HCC in situ model in mice.
Results: We found that HSCs promoted T-cell apoptosis and decreased their proliferation, inhibited dendritic cell (DC) maturation, and induced myeloid-derived suppressor cell (MDSC) expansion through the C3 pathway in vitro. In addition, the knockdown of C3 suppressed HSC-promoted HCC development in the orthotopic transplantation tumor model of HCC in mice.
Conclusion: These findings provide more insights into the immunomodulatory roles of HSCs in HCC progression and indicate that modulation of the C3 pathway might be a novel therapeutic approach for liver cancer.
Keywords: hepatocellular carcinoma, hepatic stellate cells, complement C3, myeloid-derived suppressor cells, T cells