111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

包覆吐温 80、加载有钩藤碱的 mPEG-PLGA 纳米颗粒可用于阿尔茨海默氏病的初步研究
Authors Xu R, Wang J, Xu J, Song X, Huang H, Feng Y, Fu C
Received 1 November 2019
Accepted for publication 1 February 2020
Published 18 February 2020 Volume 2020:15 Pages 1149—1160
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S236922
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Thomas Webster
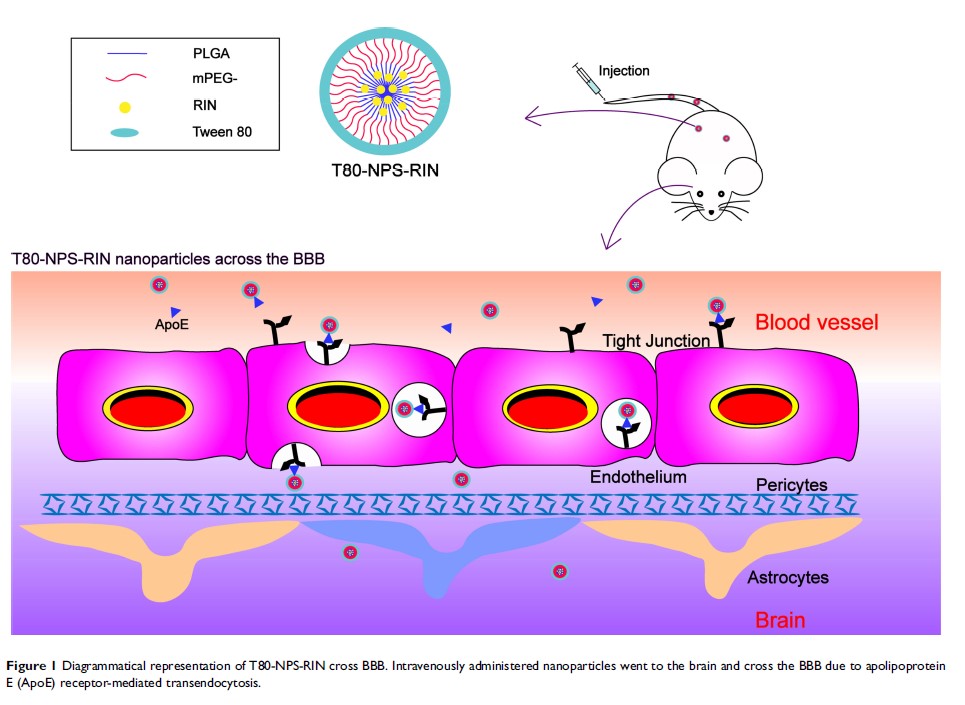
Purpose: Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is a growing concern in the modern society. The current drugs approved by FDA are not very promising. Rhynchophylline (RIN) is a major active tetracyclic oxindole alkaloid stem from traditional Chinese medicine uncaria species, which has potential activities beneficial for the treatment of AD. However, the application of rhynchophylline for AD treatment is restricted by the low water solubility, low concentration in brain tissue and low bioavailability. And there is no study of brain-targeting therapy with RIN. In this work, we prepared rhynchophylline loaded methoxy poly (ethylene glycol)–poly (dl-lactide-co-glycolic acid) (mPEG-PLGA) nanoparticles (NPS-RIN), which coupled with Tween 80 (T80) further for brain targeting delivery (T80-NPS-RIN).
Methods: Preparation and characterization of T80-NPS-RIN were followed by the detection of transportation across the blood–brain barrier (BBB) model in vitro, biodistribution and neuroprotective effects of nanoparticles.
Results: The results indicated T80-NPS-RIN could usefully assist RIN to pass through the BBB to the brain. T80-NPS-RIN treatment regulated the activity of neurons in vitro.
Conclusion: The presented data confirmed that rhynchophylline encapsulated mPEG-PLGA nanoparticles coated with Tween 80 could across through the BBB and exhibited efficient neuroprotective effects. The T80-NPS-RIN nanoparticles have a chance to be an alternative drug to the therapy of AD.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease, rhynchophylline, nanoparticles, blood–brain barrier, neuroprotective effect