111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

中国汉族人群谷胱甘肽 S-转移酶(GST)多态性与精神分裂症的关联
Authors Yan C, Duan L, Fu C, Tian C, Zhang B, Shao X, Zhu G
Received 17 October 2019
Accepted for publication 27 January 2020
Published 18 February 2020 Volume 2020:16 Pages 479—487
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/NDT.S235043
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Jun Chen
Background: Glutathione S-transferase (GST) is an important antioxidant enzyme in the body. The weakening of the antioxidant system causes damage to the cells and tissues that make up the organism, adversely affects the function of the nervous system, and ultimately leads to schizophrenia (SCZ). Previous studies have yielded inconsistent results across different ethnic populations.
Purpose: This case–control study was carried out to investigate whether genetic polymorphisms in GST could be associated with SCZ in the Chinese Han population.
Patients and Methods: A total of 794 participants, including 379 SCZ patients (case group) and 415 healthy individuals (control group), were genotyped by polymerase chain reaction-restriction fragment length for polymorphisms in GST genes.
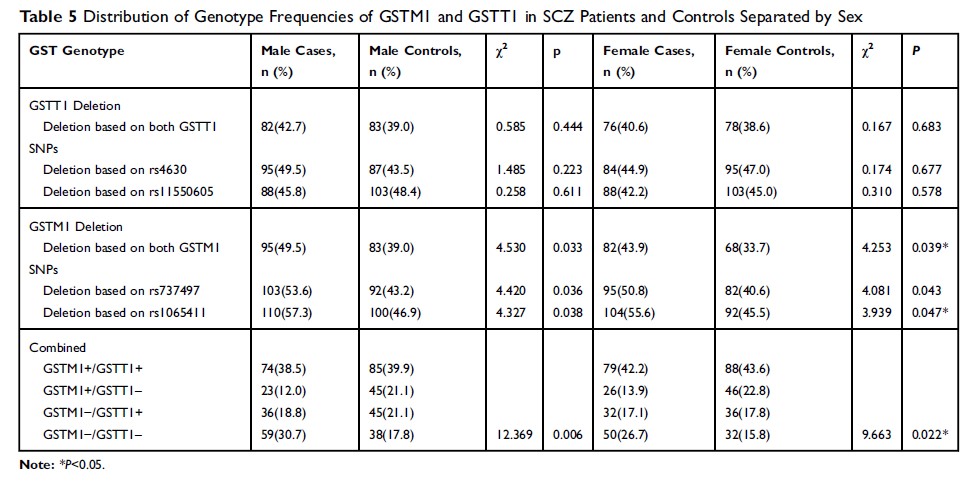
Results: The study found that the frequency of the GSTM1 null genotype was higher in case group than control group (p =0.003). The frequency of the GSTM1 and GSTT1 double null genotype was also higher in case group than control group (p =0.008).
Conclusion: We conclude that the GSTM1 null genotype and the GSTM1 and GSTT1 double null genotype may be related to the onset of SCZ in Chinese Han population.
Keywords: glutathione transferase, gene polymorphisms, schizophrenia