111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

长非编码 RNA TMPO-AS1 通过 miR-140-5p 海绵化及诱导 SOX4 介导的上皮间质转化促进胃癌细胞迁移和侵袭
Authors Sun Y, Han C
Received 24 October 2019
Accepted for publication 21 January 2020
Published 20 February 2020 Volume 2020:12 Pages 1261—1268
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S235898
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Lu-Zhe Sun
Background: Mounting evidence show that long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) play critical roles in the progression of various human cancers, including gastric cancer (GC), a common gastrointestinal tumor. In this study, the biological functions of lncRNA TMPO-AS1 in GC were studied.
Methods: TMPO-AS1 and miR-140-5p expression levels were detected in GC tissues and cell lines by RT-qPCR analysis. Knockdown or overexpression of TMPO-AS1 was conducted to evaluate the effects of TMPO-AS1 on the malignant behaviors of GC cells. Bioinformatic prediction and dual-luciferase reporter assay were performed to investigate the direct interaction between TMPO-AS1 and miR-140-5p in GC.
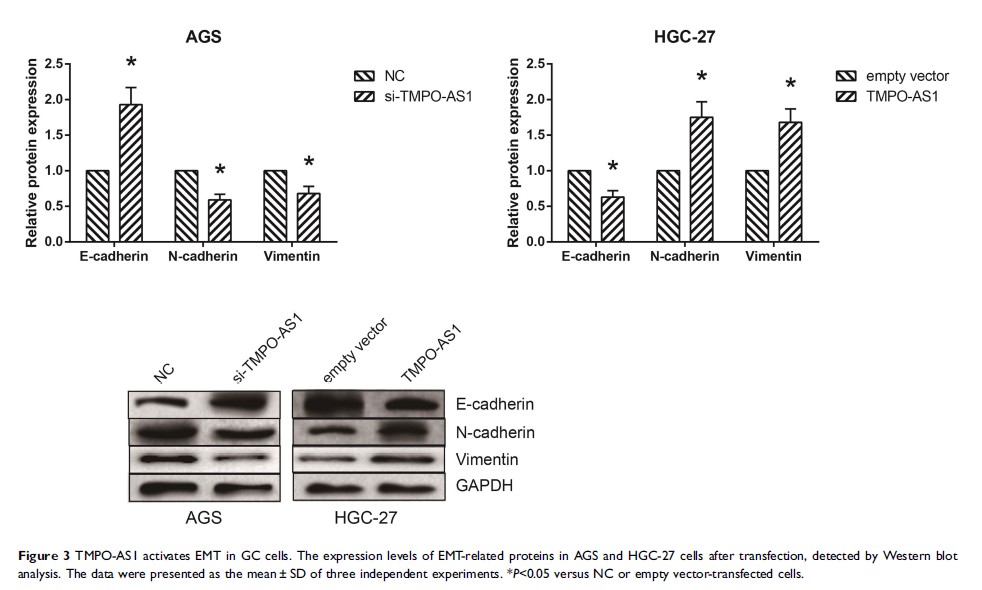
Results: We observed that TMPO-AS1 was up-regulated in GC tissues, and high TMPO-AS1 expression in GC patients was closely correlated with aggressive clinicopathologic characteristics and poor overall survival. Functionally, gain- and loss-of-function studies showed that TMPO-AS1 overexpression enhanced the proliferation, migration, invasion and EMT of GC cells in vitro, whereas knockdown of TMPO-AS1 inhibited these malignant traits. Importantly, we demonstrated that TMPO-AS1 could function as a competing endogenous RNA (ceRNA) by sponging miR-140-5p in GC cells, thereby diminishing the inhibition on SOX4, an EMT regulator.
Conclusion: Our findings indicated that TMPO-AS1 promotes GC progression partly by regulating miR-140-5p/SOX4 axis, and may serve as a novel therapeutic target for GC.
Keywords: gastric cancer, long non-coding RNA TMPO-AS1, miR-140-5p, SOX4, EMT