111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

由叶酸修饰的 MPEG-PCL 自组装胶束进行肿瘤靶向姜黄素递送,用于大肠癌治疗
Authors Hu Y, He Y, Ji J, Zheng S, Cheng Y
Received 28 September 2019
Accepted for publication 2 January 2020
Published 21 February 2020 Volume 2020:15 Pages 1239—1252
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S232777
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Mian Wang
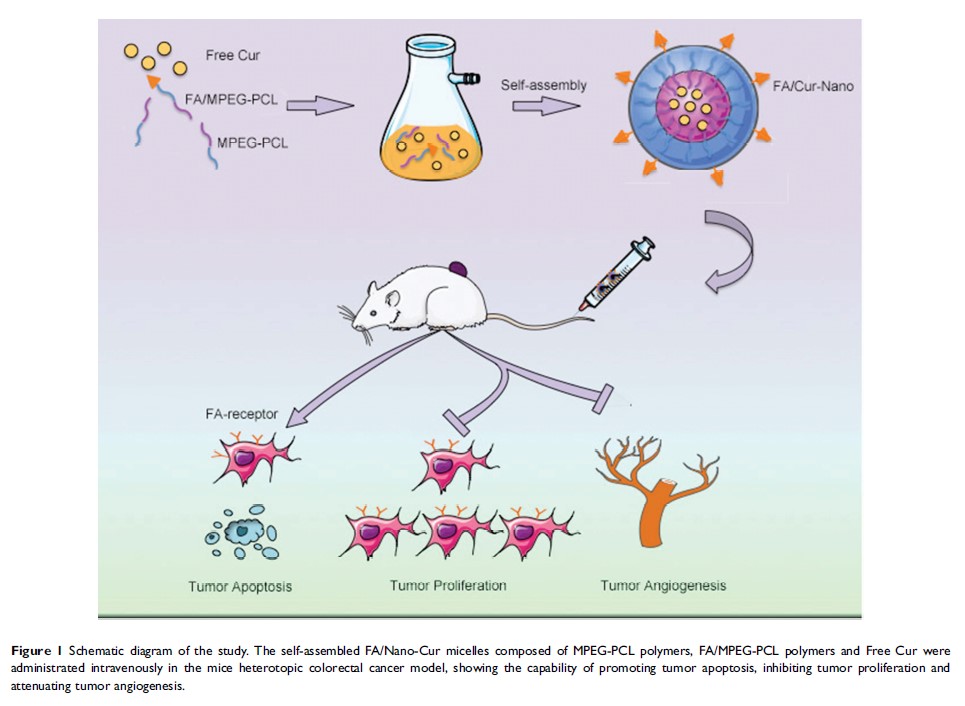
Introduction: Curcumin (Cur) is a natural extract of Asian spice Curcumin longa , showing multi-targeting capability and low toxicity in anti-tumor activities. The low bioavailability restricts its application as a therapeutic agent. Folate (FA) receptors are highly expressed in many malignant tumors while low expressed in normal tissue. Herein, we developed a self-assembled FA modified MPEG-PCL micelle to incorporate Cur (FA/Nano-Cur) and applied it for colorectal cancer therapy.
Methods: We prepared FA/Nano-Cur micelles and identified their characteristics. The drug release behavior, pharmacokinetics and in vitro anti-tumor activities of FA/Nano-Cur were studied. Furthermore, the in vivo anti-tumor ability assessment and anti-tumor mechanisms investigation were carried out in murine colorectal cancer model.
Results: FA/Nano-Cur micelles had an average particle size of 30.47 nm. Elongated T 1/2 and larger AUC were found in FA/Nano-Cur group than that in the Free Cur group. MTT assay and apoptotic study indicated the growth inhibitory effect and pro-apoptotic effect of FA/Nano-Cur were the most significant among all treatments. Moreover, the in vivo study demonstrated that FA/Nano-Cur micelles exhibited a much stronger effect to suppress tumor growth, promote tumor apoptosis and attenuate tumor angiogenesis than Free Cur and Nano-Cur micelles.
Conclusion: The present study demonstrated FA/Nano-Cur micelles might be a promising therapeutic agent in colorectal cancer treatment with distinctive advantages of improved bioavailability, sustained drug release, tumor-targeted delivery and low toxicity.
Keywords: curcumin, colorectal cancer, folate, nanoformulation, apoptosis, angiogenesis