111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

Geniposide 可平衡氧化还原信号,从而介导胰岛 β 细胞中葡萄糖刺激的胰岛素分泌
Authors Liu C, Hao Y, Yin F, Liu J
Received 2 December 2019
Accepted for publication 23 January 2020
Published 25 February 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 509—520
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DMSO.S240794
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Antonio Brunetti
Purpose: To investigate the effect of geniposide on the biosynthesis of insulin and the expression protein disulfide isomerase (PDI) and endoplasmic reticulum oxidoreductin 1 (ERO1) in the presence of low (5 mM) and high (25 mM) glucose in pancreatic β cells.
Methods: The content of insulin was measured by ELISA, the number of SH groups was determined with the classical chromogenic reagent, 5,5ʹ-dithiobis-(2-nitrobenzoic) acid (DTNB; also known as Ellman’s reagent), the expressions of PDI and ERO1 were analyzed by Western blot.
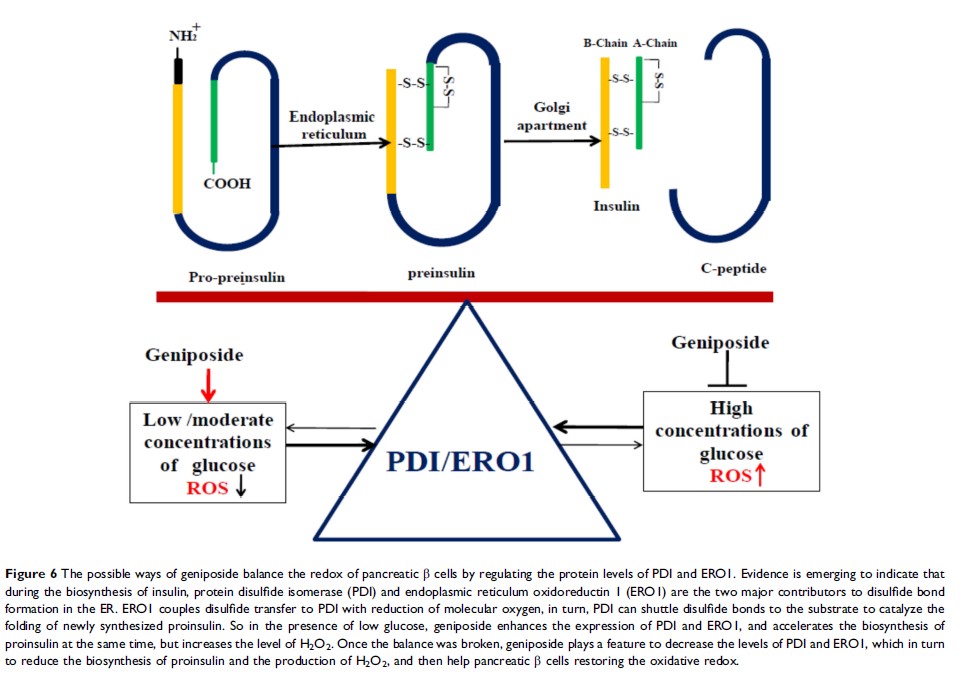
Results: Geniposide played contrary roles on the accumulation of H 2O 2, the ratio of GSH/GSSG and the thiol–disulfide balance in the presence of low (5 mM) and high (25 mM) glucose in rat pancreatic INS-1 cells. Geniposide also regulated the protein levels of protein disulfide isomerase (PDI) and endoplasmic reticulum oxidoreductin1 (ERO1), the two key enzymes for the production of H 2O 2 during the biosynthesis of insulin in INS-1 cells.
Conclusion: Geniposide affects glucose-stimulated insulin secretion by modulating the thiol–disulfide balance that is controlled by the redox signaling in pancreatic β cells.
Keywords: endoplasmic reticulum oxidoreductin1, ERO1, geniposide, protein disulfide isomerase, PDI, glucose-stimulated insulin secretion, GSIS, type 2 diabetes mellitus, T2DM